CDK9 inhibitors in cancer research
- PMID: 35814933
- PMCID: PMC9215160
- DOI: 10.1039/d2md00040g
CDK9 inhibitors in cancer research
Abstract
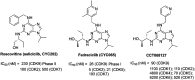
Cyclin dependent kinase 9 (CDK9) plays an essential role in regulating transcriptional elongation. Aberrations in CDK9 activity have been observed in various cancers, which make CDK9 an attractive therapeutic target for cancers. This led to an intensive development of small-molecule CDK9 inhibitors or new emerging strategies, such as proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs). Here, we review the CDK9 modulators in cancer not only for research purposes, but also for therapeutic applications.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Recent Developments in the Biology and Medicinal Chemistry of CDK9 Inhibitors: An Update.J Med Chem. 2020 Nov 25;63(22):13228-13257. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c00744. Epub 2020 Sep 17. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32866383 Review.
-
Discovery of Wogonin-based PROTACs against CDK9 and capable of achieving antitumor activity.Bioorg Chem. 2018 Dec;81:373-381. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.08.028. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Bioorg Chem. 2018. PMID: 30196207
-
Molecular Insights on Selective and Specific Inhibitors of Cyclin Dependent Kinase 9 Enzyme (CDK9) for the Purpose of Cancer Therapy.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2023;23(4):383-403. doi: 10.2174/1871520622666220615125826. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 35708082 Review.
-
Chemically induced degradation of CDK9 by a proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC).Chem Commun (Camb). 2017 Jul 4;53(54):7577-7580. doi: 10.1039/c7cc03879h. Chem Commun (Camb). 2017. PMID: 28636052 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (Cdk9) of fission yeast is activated by the CDK-activating kinase Csk1, overlaps functionally with the TFIIH-associated kinase Mcs6, and associates with the mRNA cap methyltransferase Pcm1 in vivo.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Feb;26(3):777-88. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.3.777-788.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16428435 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Safety and Efficacy of a Selective Inhibitor of Cyclin-dependent Kinase 9 (KB-0742) in Patients with Recurrent or Metastatic Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma.Cancer Res Commun. 2025 May 1;5(5):767-773. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-25-0015. Cancer Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40277179 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Discovery of KB-0742, a Potent, Selective, Orally Bioavailable Small Molecule Inhibitor of CDK9 for MYC-Dependent Cancers.J Med Chem. 2023 Dec 14;66(23):15629-15647. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c01233. Epub 2023 Nov 15. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37967851 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in KEAP1-based PROTACs as emerging therapeutic modalities: Structural basis and progress.Redox Biol. 2025 Sep;85:103781. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103781. Epub 2025 Jul 21. Redox Biol. 2025. PMID: 40714402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New strategies in soft tissue sarcoma treatment.J Hematol Oncol. 2024 Sep 2;17(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s13045-024-01580-3. J Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39218932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CDK9 Inhibition by Dinaciclib Is a Therapeutic Vulnerability in Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma.Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 13;30(18):4179-4189. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-1097. Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39052240 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

