The mir-21 Inhibition Enhanced HUVEC Cellular Viability during Hypoxia-Reoxygenation Injury by Regulating PDCD4
- PMID: 35814945
- PMCID: PMC9262501
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9661940
The mir-21 Inhibition Enhanced HUVEC Cellular Viability during Hypoxia-Reoxygenation Injury by Regulating PDCD4
Abstract
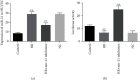
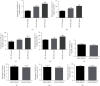
The purpose of this study was to explore the clinical value of altered plasma mir-21 expression level as a biomarker for the severity of coronary artery disease (CAD) and its molecular impact on HUVEC cellular injuries. Angiographically validated 56 patients with single-vessel CAD disease, 92 patients with double-vessel CAD, 139 complex coronary artery stenosis patients, and 56 healthy individuals (n = 343) were enrolled in this study. The expressions of plasma mir-21 were evidently and progressively higher while PDCD4 levels were significantly and steadily lower in single-, dual-, and multivessel occluded CAD patients than in healthy participants (P < 0.001). The relative expressions of mir-21 in hypoxia-reoxygenation- (HR-) exposed HUVECs were markedly upregulated, but PDCD4 concentrations were obviously downregulated as compared with normal control cells (P < 0.001). Moreover, altered circulatory mir-21 expression levels were able to significantly differentiate single- (AUC 0.893), double- (AUC 0.914), and multivessel stenosis CAD (AUC 0.933) patients from healthy subjects. Besides, the plasma mir-21 expressions in elderly (66-85 years) groups were remarkably higher than those in younger aged (25-45 years) subjects. Caspase-3 and ROS expression levels were remarkably elevated, but cellular viability noticeably declined in HR-induced HUVECs than in normoxic cells (P < 0.001). In contrast, mir-21 inhibition markedly reduced caspase-3 activity and ROS concentrations while significantly ameliorating HUVEC cellular viability in HR conditions. PDCD4 expressions in HR-exposed HUVECs were prominently decreased whereas mir-21 inhibition significantly enhanced PDCD4 levels (P < 0.001). Upregulated plasma mir-21 can be a valuable clinical biomarker for the detection of the severity of coronary artery stenosis patients. Elevated circulatory mir-21 concentrations have a positive correlation with aging. Inhibitory mir-21 evidently increased HUVEC cellular viability through upregulation of targeting PDCD4 and recommended a newer possible therapeutic molecule for the management of CAD patients.
Copyright © 2022 Md Sayed Ali Sheikh.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that he has no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

