Today's Mistakes and Tomorrow's Wisdom… In Barrett's Surveillance
- PMID: 35814973
- PMCID: PMC9209968
- DOI: 10.1159/000522376
Today's Mistakes and Tomorrow's Wisdom… In Barrett's Surveillance
Abstract
Background: Barrett's esophagus (BE) is the only known precursor lesion of esophageal adenocarcinoma, a malignancy with increasing incidence and poor survival rates. To reduce mortality, regular endoscopic surveillance of BE patients is recommended to detect neoplasia in an (endoscopically) curable stage. In this review, we aim to provide an overview of current BE surveillance strategies, its pitfalls, and potential future directions to optimize BE surveillance.
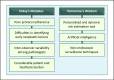
Summary: Several societal guidelines provide surveillance strategies. However, when practicing those endoscopies multiple drawbacks are encountered. Important challenges are time-consuming biopsy protocols with low adherence rates, biopsy sampling error, interobserver variability in endoscopic detection of lesions, and interobserver variability in diagnosis of dysplasia. Furthermore, the overall efficacy and cost-effectiveness of surveillance are questioned. Using novel techniques, such as artificial intelligence and personalized surveillance intervals, can help to overcome these obstacles.
Key messages: Currently, there is room for improvement in BE surveillance. Better risk-stratification is expected to reduce both patient and healthcare burdens. Personalized and dynamic surveillance intervals accompanied by novel techniques in detection and histopathological assessment of dysplasia may be tools for a change in the right direction.
Keywords: Barrett's esophagus; Cost-effectiveness; Dysplasia; Risk-stratification; Surveillance.
Copyright © 2022 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Spechler SJ, Souza RF. Barrett's esophagus. N Engl J Med. 2014;371((9)):836–45. - PubMed
-
- Hameeteman W, Tytgat GN, Houthoff HJ, van den Tweel JG. Barrett's esophagus: development of dysplasia and adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. 1989;96((5 Pt 1)):1249–56. - PubMed
-
- Yousef F, Cardwell C, Cantwell MM, Galway K, Johnston BT, Murray L. The incidence of esophageal cancer and high-grade dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Epidemiol. 2008;168((3)):237–49. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources