Sexual activity and cancer: A systematic review of prevalence, predictors and information needs among female Arab cancer survivors
- PMID: 35816027
- PMCID: PMC9786682
- DOI: 10.1111/ecc.13644
Sexual activity and cancer: A systematic review of prevalence, predictors and information needs among female Arab cancer survivors
Abstract
Introduction: The objective of this review is to synthesise and present the best available evidence on the prevalence, predictors and information needs about sexual health among female Arab cancer survivors.
Methods: The databases searched included MEDLINE, Embase and CINAHL from inception of the database until March 2020. The review was undertaken according to the JBI guidelines. Proportional meta-analysis using a random effects model was used for statistical pooling through JBI SUMARI.
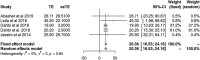
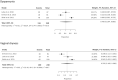
Results: Seven studies involving female Arab cancer survivors were included in the review. The overall prevalence of sexual dysfunction ranged from 16.7 to 67% (pooled estimate 51%, 95% CIs 21.7% to 80.2%). Dyspareunia and erectile dysfunction were the two main types of sexual dysfunction reported after diagnosis, and the overall prevalence ranged from 42.5% to 65% and 38% to 61%, respectively. The prevalence of vaginal dryness was ranged from 19.8% to 54.2%, and dyspareunia ranged from 22.2% to 65%. The lack of sexuality information and communication with health care providers (HCPs) was also reported in the included studies.
Conclusion: Cancer and its treatment may result in significant difficulties with sexual activity and sexual functioning among cancer survivor. Communication between the health care professionals and cancer survivors is essential to overcome this problem and improve the quality of life of female Arab cancer survivors.
Keywords: Arab; cancer; female; sexual activity; sexual dysfunction; sexuality.
© 2022 The Authors. European Journal of Cancer Care published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
R.F. who is an author on this paper is also a member of the JBI editorial board. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Male and Female Sexual Function and Dysfunction; Andrology.J Urol. 2023 May;209(5):1013-1014. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000003382. Epub 2023 Feb 22. J Urol. 2023. PMID: 37026648 No abstract available.
References
-
- Albers, L. F. , van Belzen, M. A. , van Batenburg, C. , Engelen, V. , Putter, H. , Pelger, R. C. , & Elzevier, H. W. (2020). Discussing sexuality in cancer care: Towards personalized information for cancer patients and survivors. Supportive Care in Cancer, 28(9), 1–7. 10.1007/s00520-019-05257-3 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical