Cancer type classification using plasma cell-free RNAs derived from human and microbes
- PMID: 35816095
- PMCID: PMC9273212
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.75181
Cancer type classification using plasma cell-free RNAs derived from human and microbes
Abstract
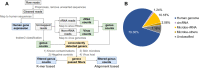
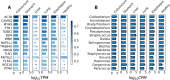
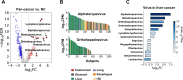
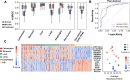
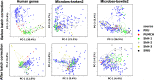
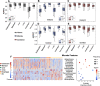
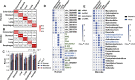
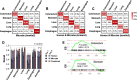
The utility of cell-free nucleic acids in monitoring cancer has been recognized by both scientists and clinicians. In addition to human transcripts, a fraction of cell-free nucleic acids in human plasma were proven to be derived from microbes and reported to have relevance to cancer. To obtain a better understanding of plasma cell-free RNAs (cfRNAs) in cancer patients, we profiled cfRNAs in ~300 plasma samples of 5 cancer types (colorectal cancer, stomach cancer, liver cancer, lung cancer, and esophageal cancer) and healthy donors (HDs) with RNA-seq. Microbe-derived cfRNAs were consistently detected by different computational methods when potential contaminations were carefully filtered. Clinically relevant signals were identified from human and microbial reads, and enriched Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways of downregulated human genes and higher prevalence torque teno viruses both suggest that a fraction of cancer patients were immunosuppressed. Our data support the diagnostic value of human and microbe-derived plasma cfRNAs for cancer detection, as an area under the ROC curve of approximately 0.9 for distinguishing cancer patients from HDs was achieved. Moreover, human and microbial cfRNAs both have cancer type specificity, and combining two types of features could distinguish tumors of five different primary locations with an average recall of 60.4%. Compared to using human features alone, adding microbial features improved the average recall by approximately 8%. In summary, this work provides evidence for the clinical relevance of human and microbe-derived plasma cfRNAs and their potential utilities in cancer detection as well as the determination of tumor sites.
Keywords: biomarker; cancer classification; cell-free RNA; computational biology; genetics; genomics; human; liquid biopsy; microbiome; systems biology.
© 2022, Chen, Jin, Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SC, YJ, SW, SX, YW, YT, YM, SZ, XL, YH, HC, YL, FX, CX, JY, XW, ZL, NZ, ZZ, ZL, PW No competing interests declared
Figures



References
-
- Abbosh C, Birkbak NJ, Wilson GA, Jamal-Hanjani M, Constantin T, Salari R, Le Quesne J, Moore DA, Veeriah S, Rosenthal R, Marafioti T, Kirkizlar E, Watkins TBK, McGranahan N, Ward S, Martinson L, Riley J, Fraioli F, Al Bakir M, Grönroos E, Zambrana F, Endozo R, Bi WL, Fennessy FM, Sponer N, Johnson D, Laycock J, Shafi S, Czyzewska-Khan J, Rowan A, Chambers T, Matthews N, Turajlic S, Hiley C, Lee SM, Forster MD, Ahmad T, Falzon M, Borg E, Lawrence D, Hayward M, Kolvekar S, Panagiotopoulos N, Janes SM, Thakrar R, Ahmed A, Blackhall F, Summers Y, Hafez D, Naik A, Ganguly A, Kareht S, Shah R, Joseph L, Marie Quinn A, Crosbie PA, Naidu B, Middleton G, Langman G, Trotter S, Nicolson M, Remmen H, Kerr K, Chetty M, Gomersall L, Fennell DA, Nakas A, Rathinam S, Anand G, Khan S, Russell P, Ezhil V, Ismail B, Irvin-Sellers M, Prakash V, Lester JF, Kornaszewska M, Attanoos R, Adams H, Davies H, Oukrif D, Akarca AU, Hartley JA, Lowe HL, Lock S, Iles N, Bell H, Ngai Y, Elgar G, Szallasi Z, Schwarz RF, Herrero J, Stewart A, Quezada SA, Peggs KS, Van Loo P, Dive C, Lin CJ, Rabinowitz M, Aerts HJWL, Hackshaw A, Shaw JA, Zimmermann BG, TRACERx consortium. PEACE consortium. Swanton C. Phylogenetic ctDNA analysis depicts early-stage lung cancer evolution. Nature. 2017;545:446–451. doi: 10.1038/nature22364. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Best MG, Sol N, Kooi I, Tannous J, Westerman BA, Rustenburg F, Schellen P, Verschueren H, Post E, Koster J, Ylstra B, Ameziane N, Dorsman J, Smit EF, Verheul HM, Noske DP, Reijneveld JC, Nilsson RJA, Tannous BA, Wesseling P, Wurdinger T. RNA-Seq of Tumor-Educated Platelets Enables Blood-Based Pan-Cancer, Multiclass, and Molecular Pathway Cancer Diagnostics. Cancer Cell. 2015;28:666–676. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.09.018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blauwkamp TA, Thair S, Rosen MJ, Blair L, Lindner MS, Vilfan ID, Kawli T, Christians FC, Venkatasubrahmanyam S, Wall GD, Cheung A, Rogers ZN, Meshulam-Simon G, Huijse L, Balakrishnan S, Quinn JV, Hollemon D, Hong DK, Vaughn ML, Kertesz M, Bercovici S, Wilber JC, Yang S. Analytical and clinical validation of a microbial cell-free DNA sequencing test for infectious disease. Nature Microbiology. 2019;4:663–674. doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0349-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

