Identification of leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 59 (LRRC59) located in the endoplasmic reticulum as a novel prognostic factor for urothelial carcinoma
- PMID: 35816851
- PMCID: PMC9287365
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2022.101474
Identification of leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 59 (LRRC59) located in the endoplasmic reticulum as a novel prognostic factor for urothelial carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Urothelial carcinoma (UC) is one of the most common cancers worldwide. The biological heterogeneity of UCs causes considerable difficulties in predicting treatment outcomes and usually leads to clinical mismanagement. The identification of more sensitive and efficient predictive biomarkers is important in the diagnosis and classification of UCs. Herein, we report leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 59 (LRRC59) located in the endoplasmic reticulum as a novel predictive factor and potential therapeutic target for UCs.
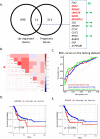
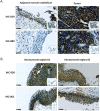
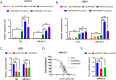
Methods: Using whole-slide image analysis in our cohort of 107 UC samples, we performed immunohistochemistry to evaluate the prognostic value of LRRC59 expression in UCs. In vitro experiments using RNAi were conducted to explore the role of LRRC59 in promoting UC cell proliferation and migration.
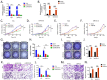
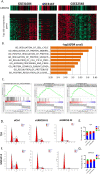
Results: A significant correlation between LRRC59 and unfavorable prognosis of UCs in our cohort was demonstrated. Subsequent clinical analysis also revealed that elevated expression levels of LRRC59 were significantly associated with higher pathological grades and advanced stages of UC. Subsequently, knockdown of LRRC59 in UM-UC-3 and T24 cells using small interfering RNA significantly inhibited cell proliferation and migration, resulting in cell cycle arrest at the G1 phase. Conversely, the overexpression of LRRC59 in UC cells enhanced cell proliferation and migration. An integrated bioinformatics analysis revealed a significant functional network of LRRC59 involving protein misfolding, ER stress, and ubiquitination. Finally, in vitro experiments demonstrated that LRRC59 modulates ER stress signaling.
Conclusions: LRRC59 expression was significantly correlated with UC prognosis. LRRC59 might not only serve as a novel prognostic biomarker for risk stratification of patients with UC but also exhibit as a potential therapeutic target in UC that warrants further investigation.
Keywords: Endoplasmic reticulum stress; Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein; Prognosis; Ubiquitination; Urothelial carcinoma.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Witjes J.A., Bruins H.M., Cathomas R., Comperat E.M., Cowan N.C., Gakis G., et al. European association of urology guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: summary of the 2020 guidelines. Eur. Urol. 2021;79(1):82–104. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.03.055. Epub 2020/05/04. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

