Protein and polypeptide mediated delivery to the eye
- PMID: 35817213
- PMCID: PMC10049092
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114441
Protein and polypeptide mediated delivery to the eye
Abstract
Hybrid or recombinant protein-polymers, peptide-based biomaterials, and antibody-targeted therapeutics are widely explored for various ocular conditions and vision correction. They have been noted for their potential biocompatibility, potency, adaptability, and opportunities for sustained drug delivery. Unique to peptide and protein therapeutics, their production by cellular translation allows their precise modification through genetic engineering. To a greater extent than drug delivery to other systems, delivery to the eye can benefit from the combination of locally-targeted administration and protein-based specificity. Consequently, a range of delivery platforms and administration methods have been exploited to address the ocular delivery of peptide and protein biomaterials. This review discusses a sample of preclinical and clinical opportunities for peptide-based drug delivery to the eye.
Keywords: Antibody; Barriers; Cornea; Elastin-like polypeptides; Lacrimal gland; Ocular; Protein; Subconjunctiva; Vitreous.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
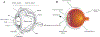
References
-
- Johannsdottir S, Jansook P, Stefansson E, Kristinsdottir IM, Fulop Z, Asgrimsdottir GM, et al., Topical drug delivery to the posterior segment of the eye: Dexamethasone concentrations in various eye tissues after topical administration for up to 15 days to rabbits, J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol. 45 (2018) 449–454.
-
- Cholkar K, Dasari SR, Pal D, Mitra AK, 1 - Eye: anatomy, physiology and barriers to drug delivery, in: Mitra AK (Ed.), Ocular Transporters and Receptors, Woodhead Publishing, 2013, pp. 1–36.
-
- Joseph RR, Venkatraman SS, Drug delivery to the eye: what benefits do nanocarriers offer?, Nanomedicine. 12 (6) (2017) 683–702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

