Receptor control by membrane-tethered ubiquitin ligases in development and tissue homeostasis
- PMID: 35817504
- PMCID: PMC10231660
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2022.03.003
Receptor control by membrane-tethered ubiquitin ligases in development and tissue homeostasis
Abstract
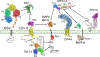
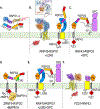
Paracrine cell-cell communication is central to all developmental processes, ranging from cell diversification to patterning and morphogenesis. Precise calibration of signaling strength is essential for the fidelity of tissue formation during embryogenesis and tissue maintenance in adults. Membrane-tethered ubiquitin ligases can control the sensitivity of target cells to secreted ligands by regulating the abundance of signaling receptors at the cell surface. We discuss two examples of this emerging concept in signaling: (1) the transmembrane ubiquitin ligases ZNRF3 and RNF43 that regulate WNT and bone morphogenetic protein receptor abundance in response to R-spondin ligands and (2) the membrane-recruited ubiquitin ligase MGRN1 that controls Hedgehog and melanocortin receptor abundance. We focus on the mechanistic logic of these systems, illustrated by structural and protein interaction models enabled by AlphaFold. We suggest that membrane-tethered ubiquitin ligases play a widespread role in remodeling the cell surface proteome to control responses to extracellular ligands in diverse biological processes.
Keywords: ATRN; BMP; BMPR1A; Cancer; Cell surface receptor; DVL; Development; E3; Endocytosis; FZD; Frizzled; HSPG; Hedgehog; Heparan sulfate proteoglycan; LGR; LRP6; MARCH; MEGF8; MGRN1; MMM; MOSMO; Melanocortin; Membrane-tethered; Morphogen; PROTAC; Patterning; Primary cilium; Protein degradation; R-spondin; RING; RNF43; RSPO; Regeneration; Signaling; Smoothened; Stem cells; Tissue homeostasis; Ubiquitin ligase; Ubiquitylation; WNT; ZNRF3.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
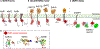
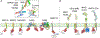
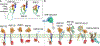
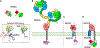
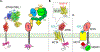
Similar articles
-
Structural and molecular basis of ZNRF3/RNF43 transmembrane ubiquitin ligase inhibition by the Wnt agonist R-spondin.Nat Commun. 2013;4:2787. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3787. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 24225776 Free PMC article.
-
USP42 protects ZNRF3/RNF43 from R-spondin-dependent clearance and inhibits Wnt signalling.EMBO Rep. 2021 May 5;22(5):e51415. doi: 10.15252/embr.202051415. Epub 2021 Mar 30. EMBO Rep. 2021. PMID: 33786993 Free PMC article.
-
R-spondins can potentiate WNT signaling without LGRs.Elife. 2018 Feb 6;7:e33126. doi: 10.7554/eLife.33126. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29405118 Free PMC article.
-
The RSPO-LGR4/5-ZNRF3/RNF43 module in liver homeostasis, regeneration, and disease.Hepatology. 2022 Sep;76(3):888-899. doi: 10.1002/hep.32328. Epub 2022 Feb 20. Hepatology. 2022. PMID: 35006616 Review.
-
Post-translational Wnt receptor regulation: Is the fog slowly clearing?: The molecular mechanism of RNF43/ZNRF3 ubiquitin ligases is not yet fully elucidated and still controversial.Bioessays. 2021 Apr;43(4):e2000297. doi: 10.1002/bies.202000297. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Bioessays. 2021. PMID: 33569855 Review.
Cited by
-
R-Spondin 2 governs Xenopus left-right body axis formation by establishing an FGF signaling gradient.Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 2;15(1):1003. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44951-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38307837 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt signalosomes: What we know that we do not know.Bioessays. 2025 Feb;47(2):e2400110. doi: 10.1002/bies.202400110. Epub 2024 Nov 9. Bioessays. 2025. PMID: 39520379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The importance of protein domain mutations in cancer therapy.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 9;10(6):e27655. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27655. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38509890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling pathways associated with Lgr6 to regulate osteogenesis.Bone. 2024 Oct;187:117207. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2024.117207. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Bone. 2024. PMID: 39033993 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into the LGR4-RSPO2-ZNRF3 complexes regulating WNT/β-catenin signaling.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 3;16(1):362. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55431-3. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39753551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acebron Sergio P., Karaulanov Emil, Berger Birgit S., Huang Ya-Lin, and Niehrs Christof. 2014. “Mitotic Wnt Signaling Promotes Protein Stabilization and Regulates Cell Size.” Molecular Cell 54 (4): 663–74. - PubMed
-
- Aoki Motoko, Kiyonari Hiroshi, Nakamura Harukazu, and Okamoto Hitoshi. 2008. “R-spondin2 Expression in the Apical Ectodermal Ridge Is Essential for Outgrowth and Patterning in Mouse Limb Development.” Development, Growth & Differentiation 50 (2): 85–95. - PubMed
-
- Aoki Motoko, Mieda Michihiro, Ikeda Toshio, Hamada Yoshio, Nakamura Harukazu, and Okamoto Hitoshi. 2007. “R-spondin3 Is Required for Mouse Placental Development.” Developmental Biology 301 (1): 218–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

