Nanoparticles in the diagnosis and treatment of vascular aging and related diseases
- PMID: 35817770
- PMCID: PMC9272665
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-022-01082-z
Nanoparticles in the diagnosis and treatment of vascular aging and related diseases
Abstract
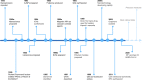
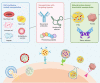
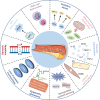
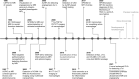
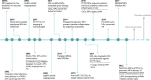
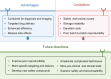
Aging-induced alternations of vasculature structures, phenotypes, and functions are key in the occurrence and development of vascular aging-related diseases. Multiple molecular and cellular events, such as oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, vascular inflammation, cellular senescence, and epigenetic alterations are highly associated with vascular aging physiopathology. Advances in nanoparticles and nanotechnology, which can realize sensitive diagnostic modalities, efficient medical treatment, and better prognosis as well as less adverse effects on non-target tissues, provide an amazing window in the field of vascular aging and related diseases. Throughout this review, we presented current knowledge on classification of nanoparticles and the relationship between vascular aging and related diseases. Importantly, we comprehensively summarized the potential of nanoparticles-based diagnostic and therapeutic techniques in vascular aging and related diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, cerebrovascular diseases, as well as chronic kidney diseases, and discussed the advantages and limitations of their clinical applications.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of Vascular Aging.Circ Res. 2018 Sep 14;123(7):849-867. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.311378. Circ Res. 2018. PMID: 30355080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Signaling Pathways of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Development of Senescence and Aging Phenotypes in Cardiovascular Disease.Cells. 2019 Nov 4;8(11):1383. doi: 10.3390/cells8111383. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31689891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial cell senescence in aging-related vascular dysfunction.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019 Jul 1;1865(7):1802-1809. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.08.008. Epub 2018 Aug 18. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019. PMID: 31109450 Review.
-
Nrf2 in early vascular ageing: Calcification, senescence and therapy.Clin Chim Acta. 2020 Jun;505:108-118. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.02.026. Epub 2020 Feb 22. Clin Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 32097628 Review.
-
Senescence mechanisms and targets in the heart.Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Mar 25;118(5):1173-1187. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab161. Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 33963378 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Obesity: pathophysiology and therapeutic interventions.Mol Biomed. 2025 Apr 25;6(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s43556-025-00264-9. Mol Biomed. 2025. PMID: 40278960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection and Elimination of Senescent Cells with a Self-Assembled Senescence-Associated β-Galactosidase-Activatable Nanophotosensitizer.J Med Chem. 2024 Jan 11;67(1):234-244. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c01306. Epub 2023 Dec 19. J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38113190 Free PMC article.
-
Developments in Emerging Topical Drug Delivery Systems for Ocular Disorders.Curr Drug Res Rev. 2024;16(3):251-267. doi: 10.2174/0125899775266634231213044704. Curr Drug Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 38158868 Review.
-
A Critical Review Examining the Characteristics of Modified Concretes with Different Nanomaterials.Materials (Basel). 2024 Jan 13;17(2):409. doi: 10.3390/ma17020409. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38255577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomimetic Ghost Nanomedicine-Based Optotheranostics for Cancer.Nano Lett. 2024 Jul 10;24(27):8217-8231. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c01534. Epub 2024 Jun 7. Nano Lett. 2024. PMID: 38848540 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

