Translational fidelity and growth of Arabidopsis require stress-sensitive diphthamide biosynthesis
- PMID: 35817801
- PMCID: PMC9273596
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-31712-7
Translational fidelity and growth of Arabidopsis require stress-sensitive diphthamide biosynthesis
Abstract
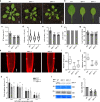
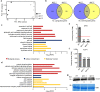
Diphthamide, a post-translationally modified histidine residue of eukaryotic TRANSLATION ELONGATION FACTOR2 (eEF2), is the human host cell-sensitizing target of diphtheria toxin. Diphthamide biosynthesis depends on the 4Fe-4S-cluster protein Dph1 catalyzing the first committed step, as well as Dph2 to Dph7, in yeast and mammals. Here we show that diphthamide modification of eEF2 is conserved in Arabidopsis thaliana and requires AtDPH1. Ribosomal -1 frameshifting-error rates are increased in Arabidopsis dph1 mutants, similar to yeast and mice. Compared to the wild type, shorter roots and smaller rosettes of dph1 mutants result from fewer formed cells. TARGET OF RAPAMYCIN (TOR) kinase activity is attenuated, and autophagy is activated, in dph1 mutants. Under abiotic stress diphthamide-unmodified eEF2 accumulates in wild-type seedlings, most strongly upon heavy metal excess, which is conserved in human cells. In summary, our results suggest that diphthamide contributes to the functionality of the translational machinery monitored by plants to regulate growth.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
K.M. and U.B. are employed by Roche which has an interest in the diagnosis and treatment of human diseases, and they are co-inventors on patent applications related to diphthamide analyses in oncology. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Diphthamide formation in Arabidopsis requires DPH1-interacting DPH2 for light and oxidative stress resistance.Plant Physiol. 2025 Mar 28;197(4):kiaf128. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiaf128. Plant Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40200557
-
The amidation step of diphthamide biosynthesis in yeast requires DPH6, a gene identified through mining the DPH1-DPH5 interaction network.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(2):e1003334. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003334. Epub 2013 Feb 28. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23468660 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into diphthamide, key diphtheria toxin effector.Toxins (Basel). 2013 May 3;5(5):958-68. doi: 10.3390/toxins5050958. Toxins (Basel). 2013. PMID: 23645155 Free PMC article.
-
The diphthamide modification pathway from Saccharomyces cerevisiae--revisited.Mol Microbiol. 2014 Dec;94(6):1213-26. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12845. Epub 2014 Nov 17. Mol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25352115 Review.
-
Diphthamide - a conserved modification of eEF2 with clinical relevance.Trends Mol Med. 2024 Feb;30(2):164-177. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2023.11.008. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Trends Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38097404 Review.
Cited by
-
Yeast gene KTI13 (alias DPH8) operates in the initiation step of diphthamide synthesis on elongation factor 2.Microb Cell. 2023 Aug 8;10(9):195-203. doi: 10.15698/mic2023.09.804. eCollection 2023 Sep 4. Microb Cell. 2023. PMID: 37662670 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Integrity of Radical SAM Enzyme Dph1•Dph2 Requires Non-Canonical Cofactor Motifs with Tandem Cysteines.Biomolecules. 2024 Apr 11;14(4):470. doi: 10.3390/biom14040470. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38672486 Free PMC article.
-
What, where, and how: Regulation of translation and the translational landscape in plants.Plant Cell. 2024 May 1;36(5):1540-1564. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koad197. Plant Cell. 2024. PMID: 37437121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DPH1 Gene Mutations Identify a Candidate SAM Pocket in Radical Enzyme Dph1•Dph2 for Diphthamide Synthesis on EF2.Biomolecules. 2023 Nov 16;13(11):1655. doi: 10.3390/biom13111655. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38002337 Free PMC article.
-
DPH1 and DPH2 variants that confer susceptibility to diphthamide deficiency syndrome in human cells and yeast models.Dis Model Mech. 2023 Sep 1;16(9):dmm050207. doi: 10.1242/dmm.050207. Epub 2023 Sep 22. Dis Model Mech. 2023. PMID: 37675463 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

