Deep Brain Stimulation for Depression
- PMID: 35817944
- PMCID: PMC9587188
- DOI: 10.1007/s13311-022-01270-3
Deep Brain Stimulation for Depression
Abstract
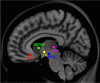
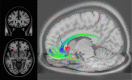
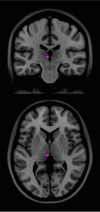
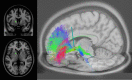
Deep brain stimulation has been extensively studied as a therapeutic option for treatment-resistant depression (TRD). DBS across different targets is associated with on average 60% response rates in previously refractory chronically depressed patients. However, response rates vary greatly between patients and between studies and often require extensive trial-and-error optimizations of stimulation parameters. Emerging evidence from tractography imaging suggests that targeting combinations of white matter tracts, rather than specific grey matter regions, is necessary for meaningful antidepressant response to DBS. In this article, we review efficacy of various DBS targets for TRD, which networks are involved in their therapeutic effects, and how we can use this information to improve targeting and programing of DBS for individual patients. We will also highlight how to integrate these DBS network findings into developing adaptive stimulation and optimal trial designs.
Keywords: Deep brain stimulation; Depression; Neuromodulation; Neurostimulation; Treatment-resistant depression.
© 2022. The American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics, Inc.
Figures
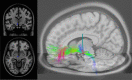
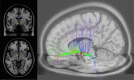
References
-
- WHO. Depression fact sheet. 2012.
-
- Rush AJ, Trivedi MH, Wisniewski SR, Nierenberg AA, Stewart JW, Warden D, et al. Acute and longer-term outcomes in depressed outpatients requiring one or several treatment steps: a STAR*D report. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(11):1905–1917. - PubMed
-
- Thase ME, Schwartz TL. Using mechanism of action to choose medications for treatment-resistant depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(9):e1147. - PubMed
-
- Mayberg HS, Lozano AM, Voon V, McNeely HE, Seminowicz D, Hamani C, et al. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neuron. 2005;45(5):651–660. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

