Validity of Estimated Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Patients With Primary Breast Cancer
- PMID: 35818548
- PMCID: PMC9270626
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2022.05.003
Validity of Estimated Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Patients With Primary Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: Estimated peak oxygen consumption (Vo2peak) is widely used in oncology; however, estimated Vo2peak equations were developed in noncancer settings.
Objectives: The aim of this study was to evaluate the validity of estimated Vo2peak in women with primary breast cancer and to develop oncology-specific estimated Vo2peak equations.
Methods: Vo2peak was directly measured (TrueOne 2400, Parvo Medics) during 380 cardiopulmonary exercise tests in women previously treated for breast cancer (mean age: 59 ± 10 years; 3.1 ± 1.2 years post-therapy). The American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM), the Fitness Registry and the Importance of Exercise National Database (FRIEND), and heart failure (HF)-FRIEND equations were used to estimate Vo2peak. New equations were developed using patient and peak (Oncpeak) or submaximal (Oncsub) exercise test characteristics.
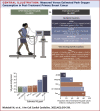
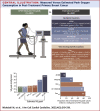
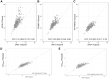
Results: The median differences between measured and estimated Vo2peak were 7.0 mL O2·kg-1·min-1, 3.9 mL O2·kg-1·min-1, and -0.2 mL O2·kg-1·min-1 for ACSM, FRIEND, and HF-FRIEND, respectively. The number of estimated Vo2peak values within ±3.5 mL O2·kg-1·min-1 of the measured values was 70 (18%), 164 (43%), and 306 (81%) for ACSM, FRIEND, and HF-FRIEND, respectively. The Oncpeak and OncSub models included body mass index, age, a history of chemotherapy or radiation, the peak measured heart rate, and the treadmill grade and/or speed. The median differences between measured and estimated Vo2peak were 0.02 mL O2·kg-1·min-1 (Oncpeak) and -0.2 mL O2·kg-1·min-1 (Oncsub). Eighty-six percent (n = 325) and 76% (n = 283) estimated Vo2peak values were within ±3.5 mL O2·kg-1·min-1 of the measured Vo2peak values for Oncpeak and Oncsub, respectively.
Conclusions: HF-FRIEND or oncology-specific equations could be applied to estimate Vo2peak in patients previously treated for breast cancer in settings where cardiopulmonary exercise tests are not available. (Trial Comparing the Effects of Linear Versus Nonlinear Aerobic Training in Women With Operable Breast Cancer [EXCITE]; NCT01186367.
Keywords: ACSM, American College of Sports Medicine; BMI, body mass index; CCC, Lin’s concordance correlation coefficient; CPET, cardiopulmonary exercise test; CRF, cardiorespiratory fitness; FRIEND, Fitness Registry and the Importance of Exercise National Database; HF, heart failure; Vo2peak, peak oxygen consumption; breast cancer; cancer survivorship; exercise capacity; peak oxygen consumption.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was supported by a research grant from the National Cancer Institute (R01-CA142566) awarded to Dr Jones and grants from AKTIV Against Cancer and the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Support Grant/Core Grant (P30 CA008748). Dr Jones has stock ownership in Pacylex, Inc. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Ross R., Blair S.N., Arena R., et al. Importance of assessing cardiorespiratory fitness in clinical practice: a case for fitness as a clinical vital sign: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;134:e653–e699. - PubMed
-
- ATS/ACCP ATS/ACCP Statement on cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;167:211–277. - PubMed
-
- Jones L.W., Haykowsky M.J., Swartz J.J., et al. Early breast cancer therapy and cardiovascular injury. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50:1435–1441. - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

