Determining Roe and Metz model parameters for simulating multireader multicase confidence-of-disease rating data based on real-data or conjectured Obuchowski-Rockette parameter estimates
- PMID: 35818569
- PMCID: PMC9268356
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JMI.9.4.045501
Determining Roe and Metz model parameters for simulating multireader multicase confidence-of-disease rating data based on real-data or conjectured Obuchowski-Rockette parameter estimates
Abstract
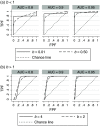
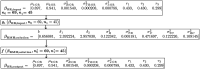
Purpose: The most frequently used model for simulating multireader multicase (MRMC) data that emulates confidence-of-disease ratings from diagnostic imaging studies has been the Roe and Metz (RM) model, proposed by Roe and Metz in 1997 and later generalized by Hillis (2012), Abbey et al. (2013), and Gallas and Hillis (2014). A problem with these models is that it has been difficult to set model parameters such that the simulated data are similar to MRMC data encountered in practice. To remedy this situation, Hillis (2018) mapped parameters from the RM model to Obuchowski-Rockette (OR) model parameters that describe the distribution of the empirical AUC outcomes computed from the RM model simulated data. We continue that work by providing the reverse mapping, i.e., by deriving an algorithm that expresses RM parameters as functions of the OR empirical AUC distribution parameters. Approach: We solve for the corresponding RM parameters in terms of the OR parameters using numerical methods. Results: An algorithm is developed that results in, at most, one solution of RM parameter values that correspond to inputted OR parameter values. The algorithm can be implemented using an R software function. Examples are provided that illustrate the use of the algorithm. A simulation study validates the algorithm. Conclusions: The resulting algorithm makes it possible to easily determine RM model parameter values such that simulated data emulate a specific real-data study. Thus, MRMC analysis methods can be empirically tested using simulated data similar to that encountered in practice.
Keywords: Obuchowski and Rockette; ROC curve; Roe and Metz; diagnostic radiology; simulated data.
© 2022 The Authors.
Figures



References
-
- Obuchowski N. A., Rockette H. E., “Hypothesis testing of diagnostic accuracy for multiple readers and multiple tests: an ANOVA approach with dependent observations,” Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. 24(2), 285–308 (1995).10.1080/03610919508813243 - DOI

