An umbrella review of systematic reviews of β-hydroxy-β-methyl butyrate supplementation in ageing and clinical practice
- PMID: 35818771
- PMCID: PMC9530546
- DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.13030
An umbrella review of systematic reviews of β-hydroxy-β-methyl butyrate supplementation in ageing and clinical practice
Abstract
The compound β-hydroxy-β-methyl butyrate (HMB) is proposed to increase or mitigate the loss of skeletal muscle and improve muscle function. We undertook a review of systematic reviews of HMB supplementation to promote gains or mitigate muscle loss in ageing and clinical populations. Following PRISMA guidelines, we searched for systematic reviews reporting the effect of HMB in our target populations. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measured lean soft-tissue mass (LSTM) was accepted as a proxy for muscle. We identified 15 systematic reviews that met our inclusion criteria, which were independently evaluated. The methodological quality of the reviews was assessed using A Measurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews (AMSTAR), and standardized effectiveness statements were generated. Five of 15 studies found some evidence that HMB augmented LSTM; the remaining 10 studies reported some evidence favouring no difference (6/10 studies) or insufficient evidence to determine an effect (4/10 studies). Of the 12 studies that evaluated strength, 4/12 found some evidence, 5/12 found some evidence of no effect with one article finding some evidence in favour of patients in peri-hospitalized and no evidence for those that are community-dwelling, 4/12 had insufficient evidence to determine an effect, and 1/12 had insufficient evidence. No]study reported a positive effect of HMB on physical function; however, 2/10 studies found some evidence favouring no effect, and 7/10 studies reported insufficient evidence to determine an effect. The effectiveness of HMB supplementation in augmenting LSTM was heterogeneous, with most reviews finding no effect or inconclusive evidence to determine an effect. Most reviews concluded that HMB supplementation did not affect strength outcome measures or studies were inconclusive. The current evidence is insufficient to assess the impact of HMB supplementation on functional outcome measures. Our analysis shows minor, inconsistent support for HMB as part of an oral nutritional supplement or as a stand-alone supplement (or combined with other amino acids) to increase or promote retention of LSTM, improve strength, and no evidence that it improves physical function in older persons or clinical populations.
Keywords: Function; Muscle mass; Sarcopenia; Strength; Supplement.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society on Sarcopenia, Cachexia and Wasting Disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Phillips reports currently (or in the prior five years) held grants from the US National Dairy Council and a contract with Roquette during the conduct of the study; personal fees from US National Dairy Council, non‐financial support from Enhanced Recovery, outside the submitted work. In addition, Dr. Phillips has a patent Canadian 3052324 issued to Exerkine, and a patent US20200230197 pending to Exerkine but reports no financial gains. All other authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

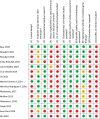
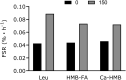
Similar articles
-
Lack of evidence for Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation in enhancing lean mass, muscle strength, and physical function in healthy adults and clinical populations: An overview of reviews.Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2025 Jun;67:155-165. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2025.03.012. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2025. PMID: 40089061 Review.
-
Nutritional interventions to improve muscle mass, muscle strength, and physical performance in older people: an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses.Nutr Rev. 2021 Jan 9;79(2):121-147. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuaa011. Nutr Rev. 2021. PMID: 32483625
-
Beta-Hydroxy-Beta-Methyl Butyrate (HMB): From Experimental Data to Clinical Evidence in Sarcopenia.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2018;19(7):668-672. doi: 10.2174/1389203718666170529105026. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2018. PMID: 28554316 Review.
-
β-Hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate and its impact on skeletal muscle mass and physical function in clinical practice: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Am J Clin Nutr. 2019 Apr 1;109(4):1119-1132. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqy373. Am J Clin Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30982854
-
Ergogenic Benefits of β-Hydroxy-β-Methyl Butyrate (HMB) Supplementation on Body Composition and Muscle Strength: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2025 Feb;16(1):e13671. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13671. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2025. PMID: 39797501 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nobiletin Improves D-Galactose-Induced Aging Mice Skeletal Muscle Atrophy by Regulating Protein Homeostasis.Nutrients. 2023 Apr 7;15(8):1801. doi: 10.3390/nu15081801. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37111020 Free PMC article.
-
Diet and Muscle Metabolism.Nutrients. 2025 May 20;17(10):1727. doi: 10.3390/nu17101727. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40431466 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Nutrients to Ameliorate Neurogenic Muscle Atrophy.Metabolites. 2022 Nov 21;12(11):1149. doi: 10.3390/metabo12111149. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36422289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interplay between gingival crevicular fluid microbiome and metabolomic profile in intensively treated people with type 1 diabetes - a combined metagenomic/metabolomic approach cross-sectional study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 2;14:1332406. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1332406. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38371896 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond Calcium and Vitamin D: Exploring Creatine, β-Hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate, Prebiotics and Probiotics in Osteosarcopenia.Nutrients. 2025 Jul 16;17(14):2332. doi: 10.3390/nu17142332. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40732957 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Choudry HA, Pan M, Karinch AM, Souba WW. Branched‐chain amino acid‐enriched nutritional support in surgical and cancer patients. J Nutr 2006;136:314–8s. - PubMed
-
- Anthony JC, Yoshizawa F, Anthony TG, Vary TC, Jefferson LS, Kimball SR. Leucine stimulates translation initiation in skeletal muscle of postabsorptive rats via a rapamycin‐sensitive pathway. Journal of Nutrition 2000;130:2413–2419. - PubMed
-
- Norton LE, Layman DK, Bunpo P, Anthony TG, Brana DV, Garlick PJ. The leucine content of a complete meal directs peak activation but not duration of skeletal muscle protein synthesis and mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in rats. Journal of Nutrition. 2009;139:1103–1109. - PubMed
-
- Baier S, Johannsen D, Abumrad N, Rathmacher JA, Nissen S, Flakoll P. Year‐long changes in protein metabolism in elderly men and women supplemented with a nutrition cocktail of beta‐hydroxy‐beta‐methylbutyrate (HMB), L‐arginine, and L‐lysine. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2009;33:71–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

