Clinical effectiveness of restorative materials for the restoration of carious primary teeth without pulp therapy: a systematic review
- PMID: 35819627
- PMCID: PMC9637592
- DOI: 10.1007/s40368-022-00725-7
Clinical effectiveness of restorative materials for the restoration of carious primary teeth without pulp therapy: a systematic review
Abstract
Purpose: To systematically search the available evidence and evaluate the clinical effectiveness of restorative materials for restoration of carious primary teeth. The findings aimed to support the European Academy of Paediatric Dentistry (EAPD) guidelines development.
Methods: Literature search was performed by searching 4 electronic databases for eligible randomised controlled clinical trials (RCTs) comparing restorative materials for the restoration of carious primary teeth up to December 28th, 2020. Quality assessment was performed with the revised Cochrane risk-of-bias tool for randomized trials (RoB 2).
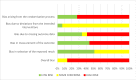
Results: Of 1685 identified articles 29 RCTs were finally deemed as eligible for inclusion. Annual failure rates were: Amalgam 1-28%; atraumatic restorative treatment 1.2-37.1%; glass-ionomer cement (GIC) 7.6-16.6%, metal-reinforced GIC 29.9%, resin-modified GIC 1.9-16.9%, high-viscosity GIC 2.9-25.6%; glass carbomer ≤ 46.2%; compomer 0-14.7%; composite resin (CR) 0-19.5%, bulk-fill CR 0-16.9%; zirconia crowns 3.3%, composite strip crowns 15%, and preformed metal crowns (Hall-Technique) 3.1%. Secondary caries, poor marginal adaptation, loss of retention, and fracture of restoration were reported as reasons for failure. Four studies were evaluated at unclear and 25 at high risk of bias. Clinical and methodological heterogeneity, and the diversity of tested materials across included studies did not allow for meta-analyses.
Conclusions: Within the limitations of this systematic review, namely, the heterogeneity and the overall high risk of bias among included studies, clear recommendations based on solid evidence for the best restorative approach in primary teeth cannot be drawn. There is a need for future thoroughly implemented RCTs evaluating restorations in primary teeth to close this knowledge gap.
Keywords: Caries; Clinical effectiveness; Dentine; Primary teeth; Restorative materials; Systematic review.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this systematic review.
Figures
References
-
- Adamczyk E, Spiechowicz E. Plaque accumulation on crowns made of various materials. Int J Prosthodont. 1990;3(3):285–291. - PubMed
-
- Alves dos Santos MP, Luiz RR, Maia LC. Randomised trial of resin-based restorations in Class I and Class II beveled preparations in primary molars: 48-month results. J Dent. 2010; 38(6): 451–459. 10.1016/j.jdent.2010.02.004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous