Decoupling the Chemical and Mechanical Strain Effect on Steering the CO2 Activation over CeO2-Based Oxides: An Experimental and DFT Approach
- PMID: 35820019
- PMCID: PMC9335529
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.2c05714
Decoupling the Chemical and Mechanical Strain Effect on Steering the CO2 Activation over CeO2-Based Oxides: An Experimental and DFT Approach
Abstract
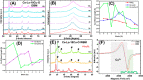
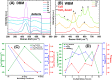
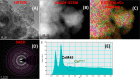
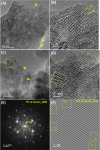
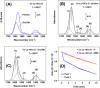
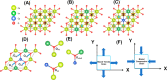
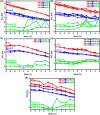
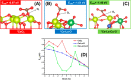
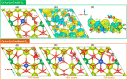
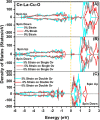
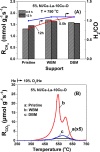
Doped ceria-based metal oxides are widely used as supports and stand-alone catalysts in reactions where CO2 is involved. Thus, it is important to understand how to tailor their CO2 adsorption behavior. In this work, steering the CO2 activation behavior of Ce-La-Cu-O ternary oxide surfaces through the combined effect of chemical and mechanical strain was thoroughly examined using both experimental and ab initio modeling approaches. Doping with aliovalent metal cations (La3+ or La3+/Cu2+) and post-synthetic ball milling were considered as the origin of the chemical and mechanical strain of CeO2, respectively. Experimentally, microwave-assisted reflux-prepared Ce-La-Cu-O ternary oxides were imposed into mechanical forces to tune the structure, redox ability, defects, and CO2 surface adsorption properties; the latter were used as key descriptors. The purpose was to decouple the combined effect of the chemical strain (εC) and mechanical strain (εM) on the modification of the Ce-La-Cu-O surface reactivity toward CO2 activation. During the ab initio calculations, the stability (energy of formation, EOvf) of different configurations of oxygen vacant sites (Ov) was assessed under biaxial tensile strain (ε > 0) and compressive strain (ε < 0), whereas the CO2-philicity of the surface was assessed at different levels of the imposed mechanical strain. The EOvf values were found to decrease with increasing tensile strain. The Ce-La-Cu-O(111) surface exhibited the lowest EOvf values for the single subsurface sites, implying that Ov may occur spontaneously upon Cu addition. The mobility of the surface and bulk oxygen anions in the lattice contributing to the Ov population was measured using 16O/18O transient isothermal isotopic exchange experiments; the maximum in the dynamic rate of 16O18O formation, Rmax(16O18O), was 13.1 and 8.5 μmol g-1 s-1 for pristine (chemically strained) and dry ball-milled (chemically and mechanically strained) oxides, respectively. The CO2 activation pathway (redox vs associative) was experimentally probed using in situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy. It was demonstrated that the mechanical strain increased up to 6 times the CO2 adsorption sites, though reducing their thermal stability. This result supports the mechanical actuation of the "carbonate"-bound species; the latter was in agreement with the density functional theory (DFT)-calculated C-O bond lengths and O-C-O angles. Ab initio studies shed light on the CO2 adsorption energy (Eads), suggesting a covalent bonding which is enhanced in the presence of doping and under tensile strain. Bader charge analysis probed the adsorbate/surface charge distribution and illustrated that CO2 interacts with the dual sites (acidic and basic ones) on the surface, leading to the formation of bidentate carbonate species. Density of states (DOS) studies revealed a significant Eg drop in the presence of double Ov and compressive strain, a finding with design implications in covalent type of interactions. To bridge this study with industrially important catalytic applications, Ni-supported catalysts were prepared using pristine and ball-milled oxides and evaluated for the dry reforming of methane reaction. Ball milling was found to induce modification of the metal-support interface and Ni catalyst reducibility, thus leading to an increase in the CH4 and CO2 conversions. This study opens new possibilities to manipulate the CO2 activation for a portfolio of heterogeneous reactions.
Keywords: CO2 activation; DFT; DRIFTS; DRM; ball milling; ceria; mechanochemistry; oxygen vacancies; strain engineering; surface tuning; ternary oxides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evolution of Oxygen Vacancy Sites in Ceria-Based High-Entropy Oxides and Their Role in N2 Activation.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 May 8;16(18):23038-23053. doi: 10.1021/acsami.3c16521. Epub 2024 Apr 29. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38684003 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Ni and Fe Doping Levels on the Nano Core-Shell Structure La2Ni2-xFexO6@CeO2 Double Perovskite Type Composite Catalysts for Dry Reforming of Methane Performance.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 Jul 2;17(26):37987-38003. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5c06220. Epub 2025 Jun 21. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 40542718
-
Catalytic methane dissociation and its non-oxidative coupling in metal-dispersed molten salt media: an ab initio molecular dynamics investigation.Mater Horiz. 2025 Jun 30;12(13):4685-4698. doi: 10.1039/d5mh00416k. Mater Horiz. 2025. PMID: 40261082
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution of Oxygen Vacancy Sites in Ceria-Based High-Entropy Oxides and Their Role in N2 Activation.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 May 8;16(18):23038-23053. doi: 10.1021/acsami.3c16521. Epub 2024 Apr 29. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38684003 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, characterization, and preliminary insights of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles into potential applications, with a focus on gas sensing.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 11;13(1):19705. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46960-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37952034 Free PMC article.
-
Engaging the Concepts of Bimetallicity and Mechanical Strain for N2 Activation: A Computational Exploration.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Oct 16;16(41):56254-56270. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c09691. Epub 2024 Oct 6. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 39370605 Free PMC article.
-
CO2 Methanation over Ni Catalysts Supported on Pr-Doped CeO2 Nanostructures Synthesized via Hydrothermal and Co-Precipitation Methods.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Jul 1;15(13):1022. doi: 10.3390/nano15131022. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40648729 Free PMC article.
-
Mid-temperature CO2 Adsorption over Different Alkaline Sorbents Dispersed over Mesoporous Al2O3.ACS Omega. 2024 Feb 28;9(10):11305-11320. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c07204. eCollection 2024 Mar 12. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38496972 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mavrikakis M.; Hammer B.; Nørskov J. K. Effect of strain on the reactivity of metal surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 2819.10.1103/physrevlett.81.2819. - DOI
-
- Sasikumar C.; Srikanth S.; Kumar R.; Alex T. C.; Mehrotra S. P.. Where Does the Energy Go in High Energy Milling. Frontiers in Mechanochemistry and Mechanical Alloying; CSIR-National Metallurgical Laboratory: Jamshedpur-831007, India, 2011.
-
- Suryanarayana C. Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2001, 46, 1–184. 10.1016/s0079-6425(99)00010-9. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

