Poziotinib for EGFR exon 20-mutant NSCLC: Clinical efficacy, resistance mechanisms, and impact of insertion location on drug sensitivity
- PMID: 35820397
- PMCID: PMC9667883
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2022.06.006
Poziotinib for EGFR exon 20-mutant NSCLC: Clinical efficacy, resistance mechanisms, and impact of insertion location on drug sensitivity
Abstract
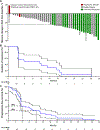
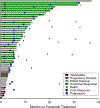
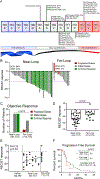
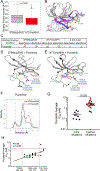
We report a phase II study of 50 advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with point mutations or insertions in EGFR exon 20 treated with poziotinib (NCT03066206). The study achieved its primary endpoint, with confirmed objective response rates (ORRs) of 32% and 31% by investigator and blinded independent review, respectively, with a median progression-free survival of 5.5 months. Using preclinical studies, in silico modeling, and molecular dynamics simulations, we found that poziotinib sensitivity was highly dependent on the insertion location, with near-loop insertions (amino acids A767 to P772) being more sensitive than far-loop insertions, an observation confirmed clinically with ORRs of 46% and 0% observed in near versus far-loop, respectively (p = 0.0015). Putative mechanisms of acquired resistance included EGFR T790M, MET amplifications, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Our data demonstrate that poziotinib is active in EGFR exon 20-mutant NSCLC, although this activity is influenced by insertion location.
Keywords: epidermal growth factor receptor; exon 20 insertion; non-small cell lung carcinoma.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The research being reported in this publication is research in which The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center has an institutional financial conflict of interest. Because M.D. Anderson is committed to the protection of human subjects and the effective management of its financial conflicts of interest in relation to its research activities, M.D. Anderson has implemented an Institutional Conflict of Interest Management and Monitoring Plan to manage and monitor the conflict of interest with respect to M.D. Anderson’s conduct of this research. M.D. Anderson, including J.P.R., M.B.N., and J.V.H., have filed a patent for the use of poziotinib for treating EGFR and HER2 mutant cancers and licensed the technology to Spectrum Pharmaceuticals (SP). J.P.R. and J.V.H. receive research support from SP and Takeda. M.D. Anderson, including M.B.N., J.P.R., and J.V.H., have a pending patent submitted for treatment of EGFR TKI-resistant NSCLC and another, including J.P.R., S.H., and J.V.H., for the classification of EGFR mutations. J.P.R. and M.B.N. have no nonfinancial competing interests. J.P.R. is now a full-time employee of AstraZeneca. J.V.H. also receives grant or research support from AstraZeneca (AZ) and GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) and has served on advisory committees for AZ, Boehringer Ingelheim (BI), Bristol Myers Squibb, Catalyst, EMD Serono, Foundation Medicine (FMI), Hengrui Therapeutics, Genentech, GSK, Guardant Health (GH), Eli Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, and Seattle Genetics. As nonfinancial competing interests, J.V.H. serves as a scientific advisor for Rexanna’s Foundation and the EGFR resisters. Y.Y.E. discloses research support from Spectrum, AstraZeneca, Takeda, Eli Lilly, Xcovery, and Tuning Point Therapeutics; and advisory role for AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, and Turning Point; and accommodation expenses from Eli Lilly. X.L. receives consultant and advisory fees from Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, and EMD Serono and research funding from Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Spectrum Pharmaceuticals. M.A. reports research funding to the M.D. Anderson Cancer Center from Genentech, Nektar Therapeutics, Merck, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Jounce Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, and Adaptimmune and receives advisory fees from GlaxoSmithKline and Shattuck Labs. V.K.L. reports advisory role fees from Takeda, Seattle Genetics, Bristol Myers Squibb, and AstraZeneca and research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, and Merck. D.L.G. reports honoraria for scientific advisory boards of AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Alethia Biotherapeutics, Lilly, and Janssen and research support from Janssen, Takeda, Ribon Therapeutics, Astellas, and AstraZeneca. G.B. receives personal fees and research funding from Amgen, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, Genentech, MedImmune, Merck, Roche, and Xcovery; research funding from Adaptimmune, Exelixis, GlaxoSmithKline, Immatics, Immunocore, Incyte, Kite Pharma, Macrogenics, Torque, AstraZeneca, Tmunity, Regeneron, Beigene, Novartis, and Repertoire Immune Medicines; and personal fees from Abbvie, Adicet, Amgen, Araid, Clovis Oncology, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myer Squibb, Celgene, Genentech, Gilead, Merck, Novartis, Roche, Virogin Biotech, Johnson & Johnson/Janssen, and Maverick Therapeutics. A.S.T. reports advisory board/consultant fees from Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Genentech, Roche, Novartis, Ariad, EMD Serono, Merck, Seattle Genetics, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sellas Life Science, Takeda, Epizyme, and Huron and receives research grants from Eli Lilly, Millennium, Polaris, Genentech, Merck, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Ariad, Epizyme, Seattle Genetics, Takeda, and EMD Serono.
Figures

Comment in
-
Location of EGFR exon 20 insertions matters.Cancer Cell. 2022 Jul 11;40(7):705-708. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2022.06.002. Cancer Cell. 2022. PMID: 35820394
References
-
- Beau-Faller M, Prim N, Ruppert AM, Nanni-Metellus I, Lacave R, Lacroix L, Escande F, Lizard S, Pretet JL, Rouquette I, et al. (2014). Rare EGFR exon 18 and exon 20 mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer on 10 117 patients: a multicentre observational study by the French ERMETIC-IFCT network. Ann Oncol 25, 126–131. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biswas A, Shukla A, Vijayan RSK, Jeyakanthan J, and Sekar K. (2017). Crystal structures of an archaeal thymidylate kinase from Sulfolobus tokodaii provide insights into the role of a conserved active site Arginine residue. J Struct Biol 197, 236–249. - PubMed
-
- Boyd S. (2005). Molecular operating environment. Chemistry World 2, 66–66.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

