IFNγ-induced PD-L1 expression in ovarian cancer cells is regulated by JAK1, STAT1 and IRF1 signaling
- PMID: 35820543
- PMCID: PMC9357219
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2022.110400
IFNγ-induced PD-L1 expression in ovarian cancer cells is regulated by JAK1, STAT1 and IRF1 signaling
Abstract
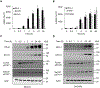
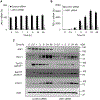
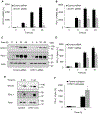
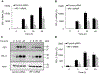
Expression of the immune checkpoint programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) is increased in ovarian cancer (OC) and correlates with poor prognosis. Interferon-γ (IFNγ) induces PD-L1 expression in OC cells, resulting in their increased proliferation and tumor growth, but the mechanisms that regulate the PD-L1 expression in OC remain unclear. Here, we show that the IFNγ-induced PD-L1 expression in OC cells is associated with increased levels of STAT1, Tyr-701 pSTAT1 and Ser-727 pSTAT1. Suppression of JAK1 and STAT1 significantly decreases the IFNγ-induced PD-L1 expression in OC cells, and STAT1 overexpression increases the IFNγ-induced PD-L1 expression. In addition, IFNγ induces expression of the transcription factor interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF1) and IRF1 suppression attenuates the IFNγ-induced gene and protein levels of PD-L1. Chromatin immunoprecipitation results show that IFNγ induces PD-L1 promoter acetylation and recruitment of STAT1, Ser-727 pSTAT1 and IRF1 in OC cells. Together, these findings demonstrate that the IFNγ-induced PD-L1 expression in OC cells is regulated by JAK1, STAT1, and IRF1 signaling, and suggest that targeting the JAK1/ STAT1/IRF1 pathway may provide a leverage to regulate the PD-L1 levels in ovarian cancer.
Keywords: Interferon-γ; Ovarian cancer; PD-L1; STAT1; Transcriptional regulation.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures
References
-
- Hamanishi J, Mandai M, Iwasaki M, Okazaki T, Tanaka Y, Yamaguchi K, et al. , Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 and tumor-infiltrating CD8 + T lymphocytes are prognostic factors of human ovarian cancer, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sd. U. S. A 104 (9) (2007) 3360–3365, 10.1073/pnas.0611533104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

