The primary macrophage chemokine, CCL2, is not necessary after a peripheral nerve injury for macrophage recruitment and activation or for conditioning lesion enhanced peripheral regeneration
- PMID: 35820932
- PMCID: PMC9277969
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-022-02497-9
The primary macrophage chemokine, CCL2, is not necessary after a peripheral nerve injury for macrophage recruitment and activation or for conditioning lesion enhanced peripheral regeneration
Abstract
Background: Peripheral nerve injuries stimulate the regenerative capacity of injured neurons through a neuroimmune phenomenon termed the conditioning lesion (CL) response. This response depends on macrophage accumulation in affected dorsal root ganglia (DRGs) and peripheral nerves. The macrophage chemokine CCL2 is upregulated after injury and is allegedly required for stimulating macrophage recruitment and pro-regenerative signaling through its receptor, CCR2. In these tissues, CCL2 is putatively produced by neurons in the DRG and Schwann cells in the distal nerve.
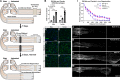
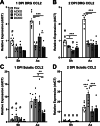
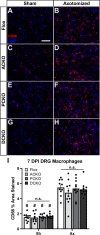
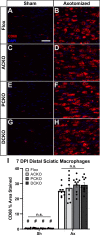
Methods: Ccl2fl/fl mice were crossed with Advillin-Cre, P0-Cre, or both to create conditional Ccl2 knockouts (CKOs) in sensory neurons, Schwann cells, or both to hypothetically remove CCL2 and macrophages from DRGs, nerves or both. CCL2 was localized using Ccl2-RFPfl/fl mice. CCL2-CCR2 signaling was further examined using global Ccl2 KOs and Ccr2gfp knock-in/knock-outs. Unilateral sciatic nerve transection was used as the injury model, and at various timepoints, chemokine expression, macrophage accumulation and function, and in vivo regeneration were examined using qPCR, immunohistochemistry, and luxol fast blue staining.
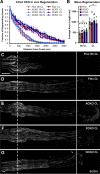
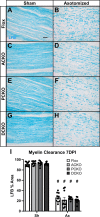
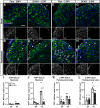
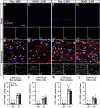
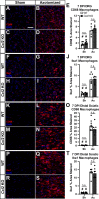
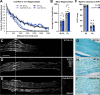
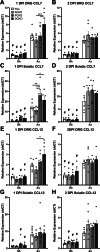
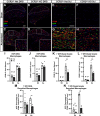
Results: Surprisingly, in all CKOs, DRG Ccl2 gene expression was decreased, while nerve Ccl2 was not. CCL2-RFP reporter mice revealed CCL2 expression in several cell types beyond the expected neurons and Schwann cells. Furthermore, macrophage accumulation, myelin clearance, and in vivo regeneration were unaffected in all CKOs, suggesting CCL2 may not be necessary for the CL response. Indeed, Ccl2 global knockout mice showed normal macrophage accumulation, myelin clearance, and in vivo regeneration, indicating these responses do not require CCL2. CCR2 ligands, Ccl7 and Ccl12, were upregulated after nerve injury and perhaps could compensate for the absence of Ccl2. Finally, Ccr2gfp knock-in/knock-out animals were used to differentiate resident and recruited macrophages in the injured tissues. Ccr2gfp/gfp KOs showed a 50% decrease in macrophages in the distal nerve compared to controls with a relative increase in resident macrophages. In the DRG there was a small but insignificant decrease in macrophages.
Conclusions: CCL2 is not necessary for macrophage accumulation, myelin clearance, and axon regeneration in the peripheral nervous system. Without CCL2, other CCR2 chemokines, resident macrophage proliferation, and CCR2-independent monocyte recruitment can compensate and allow for normal macrophage accumulation.
Keywords: Axotomy; CCL2; DRG; Macrophage; Neuroimmune; Regeneration.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neither injury induced macrophages within the nerve, nor the environment created by Wallerian degeneration is necessary for enhanced in vivo axon regeneration after peripheral nerve injury.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 May 27;21(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03132-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38802868 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of the monocyte chemokine CCL2 in dorsal root ganglion neurons causes a conditioning-like increase in neurite outgrowth and does so via a STAT3 dependent mechanism.Exp Neurol. 2016 Jan;275 Pt 1(0 1):25-37. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.09.018. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Exp Neurol. 2016. PMID: 26431741 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage biology in the peripheral nervous system after injury.Prog Neurobiol. 2019 Feb;173:102-121. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2018.12.001. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Prog Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30579784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CCL2 Mediates Neuron-Macrophage Interactions to Drive Proregenerative Macrophage Activation Following Preconditioning Injury.J Neurosci. 2015 Dec 2;35(48):15934-47. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1924-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26631474 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Cell Biology in Peripheral Nervous System Injury.Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2025 Mar;39(3):230-240. doi: 10.1177/15459683241304325. Epub 2025 Jan 2. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2025. PMID: 39744962 Review.
Cited by
-
Injury-induced activation of the endocannabinoid system promotes axon regeneration.iScience. 2023 May 5;26(6):106814. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106814. eCollection 2023 Jun 16. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37235048 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in methods for evaluating Schwann cell myelination and axonal growth in peripheral nerve regeneration via scaffolds.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Dec 7;11:1308761. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1308761. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38162183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of Magnesium Degradation on Schwannoma Cell Responses to Nerve Injury Using an In Vitro Injury Model.J Funct Biomater. 2024 Mar 31;15(4):88. doi: 10.3390/jfb15040088. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 38667545 Free PMC article.
-
Neither injury induced macrophages within the nerve, nor the environment created by Wallerian degeneration is necessary for enhanced in vivo axon regeneration after peripheral nerve injury.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 May 27;21(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03132-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38802868 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound: A Physical Stimulus with Immunomodulatory and Anti-inflammatory Potential.Ann Biomed Eng. 2024 Aug;52(8):1955-1981. doi: 10.1007/s10439-024-03523-y. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Ann Biomed Eng. 2024. PMID: 38683473 Review.
References
-
- Ramon y Cajal S. Degeneration and regeneration of the nervous system. New York: Oxford University Press; 1928.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

