Association between sensitivity to thyroid hormone indices and the risk of osteoarthritis: an NHANES study
- PMID: 35820977
- PMCID: PMC9275280
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-022-00749-1
Association between sensitivity to thyroid hormone indices and the risk of osteoarthritis: an NHANES study
Abstract
Objectives: Thyroid hormones play an instrumental role in chondrogenic differentiation and matrix maturation. However, studies investigating the relationship between thyroid function and the risk of osteoarthritis (OA) remain scarce. This study was designed to investigate the correlation between thyroid status and OA from a novel perspective of sensitivity to thyroid hormones.
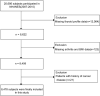
Methods: The study included 8478 people from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2007-2010. The sensitivity to thyroid hormone indices included Thyrotroph Thyroxine Resistance Index (TT4RI), Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSHI), Thyroid Feedback Quantile-based Index (TFQI), and Free Triiodothyronine /Free thyroxine (FT3/FT4), which were calculated based on serum free triiodothyronine (FT3), free thyroxine (FT4), and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). Considering the complex survey design and sample weights, we employed multivariate linear regression models and stratified analysis to evaluate the correlation between sensitivity to thyroid hormone indices and OA.
Results: Study results indicated that participants with OA had elevated TT4RI, TSHI, and TFQI levels, and lower FT3/FT4 levels compared to those with non-arthritis. After adjusting for other covariates, FT3/FT4 was negatively associated with the risk of OA (OR = 1.162, 95%CI 1.048-1.478, P = 0.021); (OR = 1.261, 95%CI 1.078-1.623, P = 0.042). In subgroup analyses stratified by gender and BMI, participants with OA had higher TFQI levels compared to those without OA in both genders. (OR = 1.491, 95%CI 1.070-2.077, P = 0.018); (OR = 2.548, 95%CI 1.929-3.365, P < 0.001). The higher TFQI levels were consistently associated with the increased prevalence of OA in the BMI (< 18.5 kg/m2) group after adjusting for different covariates, but not in other BMI groups. In, addition, TFQI performed better than FT3/FT4, TSHI, and TT4RI on ROC analyses for OA prediction.
Conclusions: The levels of FT3/FT4, TSHI, TT4RI, and TFQI are strongly associated with the prevalence of OA, which illustrates the complex correlation between the thyroid system and chondrogenic differentiation. TFQI may be used as a helpful indicator to predict OA and provide novel ideas for the evaluation and treatment of OA.
Keywords: NHANES; Osteoarthritis; Sensitivity to thyroid hormone; Thyroid.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Shuai Chen, Xiaohe Sun, Guowei Zhou, Jie Jin and Zhiwei Li declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impaired sensitivity to thyroid hormones is associated with increased body fat mass/muscle mass ratio (F/M) in the euthyroid population.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025 Apr 15;17(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s13098-025-01693-w. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025. PMID: 40234912 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between thyroid function, thyroid hormone sensitivity indices, and frailty: Insights from a large cross-sectional study.Exp Gerontol. 2025 Sep;208:112822. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2025.112822. Epub 2025 Jul 2. Exp Gerontol. 2025. PMID: 40614881
-
Impaired Sensitivity to Thyroid Hormones is Associated with Mild Cognitive Impairment in Euthyroid Patients with Type 2 Diabetes.Clin Interv Aging. 2023 Aug 3;18:1263-1274. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S413584. eCollection 2023. Clin Interv Aging. 2023. PMID: 37554512 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Metformin on Thyroid-Associated Serum Hormone Levels and Physiological Indexes: A Meta-Analysis.Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(30):3257-3265. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190918162649. Curr Pharm Des. 2019. PMID: 31533598 Review.
-
Association between thyroid hormone levels in the acute stage of stroke and risk of poststroke depression: A meta-analysis.Brain Behav. 2024 Jan;14(1):e3322. doi: 10.1002/brb3.3322. Brain Behav. 2024. PMID: 38189637 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CRP-Albumin-Lymphocyte index (CALLYI) as a risk-predicting biomarker in association with osteoarthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2025 Mar 19;27(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13075-025-03530-x. Arthritis Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40108660 Free PMC article.
-
Causal factors for osteoarthritis risk revealed by mendelian randomization analysis.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024 Aug 22;36(1):176. doi: 10.1007/s40520-024-02812-9. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024. PMID: 39172202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteoarthritis and sarcopenia-related traits: the cross-sectional study from NHANES 2011-2014 and Mendelian randomization study.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Jul 15;18(1):502. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03960-w. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 37454213 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of coffee consumption on osteoarthritis: insights from NHANES and Mendelian randomization analysis.Front Nutr. 2024 Dec 2;11:1434704. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1434704. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39691171 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired Sensitivity to Thyroid Hormones is Associated with Central Obesity in Euthyroid Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Overweight and Obesity.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Sep 11;17:3379-3396. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S472550. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 39280173 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- SEZ202107/the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine
- SEZ202107/the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine
- No. SJCX20_0054/the Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province
- 322402109D/the Fundamental Research Funds of the Central Universities
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical