The amniotic fluid proteome predicts imminent preterm delivery in asymptomatic women with a short cervix
- PMID: 35821507
- PMCID: PMC9276779
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-15392-3
The amniotic fluid proteome predicts imminent preterm delivery in asymptomatic women with a short cervix
Abstract
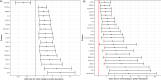
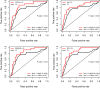
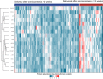
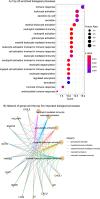
Preterm birth, the leading cause of perinatal morbidity and mortality, is associated with increased risk of short- and long-term adverse outcomes. For women identified as at risk for preterm birth attributable to a sonographic short cervix, the determination of imminent delivery is crucial for patient management. The current study aimed to identify amniotic fluid (AF) proteins that could predict imminent delivery in asymptomatic patients with a short cervix. This retrospective cohort study included women enrolled between May 2002 and September 2015 who were diagnosed with a sonographic short cervix (< 25 mm) at 16-32 weeks of gestation. Amniocenteses were performed to exclude intra-amniotic infection; none of the women included had clinical signs of infection or labor at the time of amniocentesis. An aptamer-based multiplex platform was used to profile 1310 AF proteins, and the differential protein abundance between women who delivered within two weeks from amniocentesis, and those who did not, was determined. The analysis included adjustment for quantitative cervical length and control of the false-positive rate at 10%. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was calculated to determine whether protein abundance in combination with cervical length improved the prediction of imminent preterm delivery as compared to cervical length alone. Of the 1,310 proteins profiled in AF, 17 were differentially abundant in women destined to deliver within two weeks of amniocentesis independently of the cervical length (adjusted p-value < 0.10). The decreased abundance of SNAP25 and the increased abundance of GPI, PTPN11, OLR1, ENO1, GAPDH, CHI3L1, RETN, CSF3, LCN2, CXCL1, CXCL8, PGLYRP1, LDHB, IL6, MMP8, and PRTN3 were associated with an increased risk of imminent delivery (odds ratio > 1.5 for each). The sensitivity at a 10% false-positive rate for the prediction of imminent delivery by a quantitative cervical length alone was 38%, yet it increased to 79% when combined with the abundance of four AF proteins (CXCL8, SNAP25, PTPN11, and MMP8). Neutrophil-mediated immunity, neutrophil activation, granulocyte activation, myeloid leukocyte activation, and myeloid leukocyte-mediated immunity were biological processes impacted by protein dysregulation in women destined to deliver within two weeks of diagnosis. The combination of AF protein abundance and quantitative cervical length improves prediction of the timing of delivery compared to cervical length alone, among women with a sonographic short cervix.
© 2022. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Plasma inflammatory and immune proteins as predictors of intra-amniotic infection and spontaneous preterm delivery in women with preterm labor: a retrospective study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2018 May 9;18(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12884-018-1780-7. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2018. PMID: 29743041 Free PMC article.
-
Non-invasive prediction of intra-amniotic infection and/or inflammation in patients with cervical insufficiency or an asymptomatic short cervix (≤15 mm).Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2015 Sep;292(3):579-87. doi: 10.1007/s00404-015-3684-3. Epub 2015 Mar 12. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2015. PMID: 25762201
-
Personalized assessment of cervical length improves prediction of spontaneous preterm birth: a standard and a percentile calculator.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Mar;224(3):288.e1-288.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.09.002. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 32918893 Free PMC article.
-
Transvaginal sonographic examination of the cervix in asymptomatic pregnant women: review of the literature.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2002 Mar;19(3):302-11. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-0705.2002.00645.x. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2002. PMID: 11896957 Review.
-
Cervical assessment by ultrasound for preventing preterm delivery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Sep 25;9(9):CD007235. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007235.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31553800 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Gene Expression Differences Based on Low Total 25(OH)D and Low VDBP Status with a Preterm Birth.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 8;26(10):4475. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104475. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429621 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction model for spontaneous preterm birth less than 32 weeks of gestation in low-risk women with mid-trimester short cervical length: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024 Oct 1;24(1):621. doi: 10.1186/s12884-024-06822-3. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024. PMID: 39354430 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of the expression patterns and roles of Lipocalin 2 in the reproductive system.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Apr 5;15:1365602. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1365602. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38645429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Administration of Antenatal Corticosteroids: Optimal Timing.Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2024 Jan 3;84(1):48-58. doi: 10.1055/a-2202-5363. eCollection 2024 Jan. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2024. PMID: 38205043 Free PMC article.
-
Crossing the Halfway Point: Aptamer-Based, Highly Multiplexed Assay for the Assessment of the Proteome.J Proteome Res. 2024 Nov 1;23(11):4771-4788. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c00411. Epub 2024 Jul 22. J Proteome Res. 2024. PMID: 39038188 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

