mRNA-LNP vaccines tuned for systemic immunization induce strong antitumor immunity by engaging splenic immune cells
- PMID: 35821637
- PMCID: PMC9273295
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.07.007
mRNA-LNP vaccines tuned for systemic immunization induce strong antitumor immunity by engaging splenic immune cells
Abstract
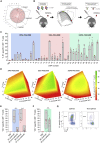
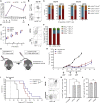
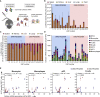
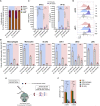
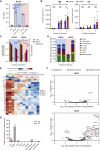
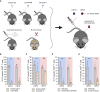
mRNA vaccines have recently proved to be highly effective against SARS-CoV-2. Key to their success is the lipid-based nanoparticle (LNP), which enables efficient mRNA expression and endows the vaccine with adjuvant properties that drive potent antibody responses. Effective cancer vaccines require long-lived, qualitative CD8 T cell responses instead of antibody responses. Systemic vaccination appears to be the most effective route, but necessitates adaptation of LNP composition to deliver mRNA to antigen-presenting cells. Using a design-of-experiments methodology, we tailored mRNA-LNP compositions to achieve high-magnitude tumor-specific CD8 T cell responses within a single round of optimization. Optimized LNP compositions resulted in enhanced mRNA uptake by multiple splenic immune cell populations. Type I interferon and phagocytes were found to be essential for the T cell response. Surprisingly, we also discovered a yet unidentified role of B cells in stimulating the vaccine-elicited CD8 T cell response. Optimized LNPs displayed a similar, spleen-centered biodistribution profile in non-human primates and did not trigger histopathological changes in liver and spleen, warranting their further assessment in clinical studies. Taken together, our study clarifies the relationship between nanoparticle composition and their T cell stimulatory capacity and provides novel insights into the underlying mechanisms of effective mRNA-LNP-based antitumor immunotherapy.
Keywords: LNP; cancer; design-of-experiments methodology; extrahepatic delivery; immunotherapy; mRNA; vaccination.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests S.B., E.V.d.V., S.S., M.M., D.V.H., and S.D.K. are employees of eTheRNA Immunotherapies NV. S.B., S.A.A.K., R.M.S., and S.D.K. have applied for patents related to this study.
Figures
References
-
- Alameh M.-G.G., Tombácz I., Bettini E., Lederer K., Sittplangkoon C., Wilmore J.R., Gaudette B.T., Soliman O.Y., Pine M., Hicks P., et al. Lipid nanoparticles enhance the efficacy of mRNA and protein subunit vaccines by inducing robust T follicular helper cell and humoral responses. Immunity. 2021;54:2877–2892.e7. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kranz L.M., Diken M., Haas H., Kreiter S., Loquai C., Reuter K.C., Meng M., Fritz D., Vascotto F., Hefesha H., et al. Systemic RNA delivery to dendritic cells exploits antiviral defence for cancer immunotherapy. Nature. 2016;534:396–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

