Prenatal diagnosis and pregnancy outcome of major structural anomalies detectable in the first trimester: A population-based cohort study in the Netherlands
- PMID: 35821640
- PMCID: PMC9796468
- DOI: 10.1111/ppe.12914
Prenatal diagnosis and pregnancy outcome of major structural anomalies detectable in the first trimester: A population-based cohort study in the Netherlands
Abstract
Background: Prenatal diagnosis of several major congenital anomalies can be achieved in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Objective: This study investigates the timing of diagnosis and pregnancy outcome of foetuses and neonates with selected structural anomalies in the Northern Netherlands over a 10-year period when the prenatal screening programme changed significantly, but no first-trimester anatomical screening was implemented.
Methods: We performed a population-based retrospective cohort study with data from the EUROCAT Northern Netherlands database on pregnancies with delivery or termination of pregnancy for fetal anomaly (TOPFA) date between 2010 and 2019. The analysis was restricted to anomalies potentially detectable in the first trimester of pregnancy in at least 50% of cases, based on previously published data. These included: anencephaly, encephalocele, spina bifida, holoprosencephaly, tricuspid/pulmonary valve atresia, hypoplastic left heart, abdominal wall and limb reduction defects, lethal skeletal dysplasia, megacystis, multiple congenital anomalies. The primary outcome was the timing of diagnosis of each structural anomaly. Information on additional investigations, genetic testing and pregnancy outcome (live birth, TOPFA and foetal/neonatal death) was also collected.
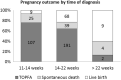
Results: A total of 478 foetuses were included; 95.0% (n = 454) of anomalies were detected prenatally and 5.0% (n = 24) postpartum. Among the prenatally detected cases, 31% (n = 141) were diagnosed before 14 weeks of gestation, 65.6% (n = 298) between 14-22 weeks and 3.3% (n = 15) after 22 weeks. Prenatal genetic testing was performed in 80.4% (n = 365) of cases with prenatally diagnosed anomalies, and the results were abnormal in 26% (n = 95). Twenty-one% (n = 102) of pregnancies resulted in live births and 62.8% (n = 300) in TOPFA. Spontaneous death occurred in 15.9% (n = 76) of cases: in-utero (6.1%, n = 29), at delivery (7.7%, n = 37) or in neonatal life (2.1%, n = 10).
Conclusion: Major structural anomalies amenable to early diagnosis in the first trimester of pregnancy are mostly diagnosed during the second trimester in the absence of a regulated first-trimester anatomical screening programme in the Netherlands and are associated with TOPFA and spontaneous death, especially in cases with underlying genetic anomalies.
Keywords: congenital anomalies; prenatal diagnosis; prenatal screening.
© 2022 The Authors. Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Introduction of a nationwide first-trimester anomaly scan in the Dutch national screening program.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2025 Apr;232(4):396.e1-396.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2024.07.026. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2025. PMID: 39067498
-
Effect of prenatal screening on trends in perinatal mortality associated with congenital anomalies before and after the introduction of prenatal screening: A population-based study in the Northern Netherlands.Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2021 Nov;35(6):654-663. doi: 10.1111/ppe.12792. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2021. PMID: 34328233 Free PMC article.
-
Early Detection of Structural Anomalies in a Primary Care Setting in the Netherlands.Fetal Diagn Ther. 2019;46(1):12-19. doi: 10.1159/000490723. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2019. PMID: 30045038 Free PMC article.
-
First and second trimester screening for fetal structural anomalies.Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018 Apr;23(2):102-111. doi: 10.1016/j.siny.2017.11.005. Epub 2017 Dec 9. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018. PMID: 29233624 Review.
-
Detection of non-cardiac fetal abnormalities on ultrasound at 11-14 weeks: systematic review and meta-analysis.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2024 Jul;64(1):15-27. doi: 10.1002/uog.27649. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2024. PMID: 38547384
Cited by
-
Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound screening for fetal structural abnormalities during the first and second trimester of pregnancy in low-risk and unselected populations.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 9;5(5):CD014715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38721874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the potential role of determinants of health on encephalocele patient outcomes - a combined retrospective study and systematic review.Childs Nerv Syst. 2024 Jun;40(6):1751-1763. doi: 10.1007/s00381-024-06312-z. Epub 2024 Feb 12. Childs Nerv Syst. 2024. PMID: 38347306
-
The status and influencing factors of abnormal fetal pregnancy outcomes in 265 cases in China: a retrospective study.PeerJ. 2024 Apr 26;12:e17284. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17284. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38685940 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal Genetic Testing in the Era of Next Generation Sequencing: A One-Center Canadian Experience.Genes (Basel). 2022 Nov 3;13(11):2019. doi: 10.3390/genes13112019. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36360262 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Congenital anomalies [Internet]. 2016. Available from: https://www.who.int/news‐room/fact‐sheets/detail/congenital‐anomalies
-
- Dolk H, Loane M, Garne E. The prevalence of congenital anomalies in Europe. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;686:349‐364. - PubMed
-
- Bardi F, Bergman JEH, Bouman K, et al. Effect of prenatal screening on trends in perinatal mortality associated with congenital anomalies before and after the introduction of prenatal screening: a population‐based study in the northern Netherlands. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2021;35:654‐663. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Syngelaki A, Chelemen T, Dagklis T, Allan L, Nicolaides KH. Challenges in the diagnosis of fetal non‐chromosomal abnormalities at 11‐13 weeks. Prenat Diagn. 2011;31:90‐102. - PubMed
-
- Kenkhuis MJA, Bakker MKK, Bardi F, et al. Effectiveness of a 12‐13 week scan for the early diagnosis of fetal congenital anomalies in the cell‐free DNA era. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2017;51:463‐469. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources