Clonal Hematopoiesis Analyses in Clinical, Epidemiologic, and Genetic Aging Studies to Unravel Underlying Mechanisms of Age-Related Dysfunction in Humans
- PMID: 35821803
- PMCID: PMC9261374
- DOI: 10.3389/fragi.2022.841796
Clonal Hematopoiesis Analyses in Clinical, Epidemiologic, and Genetic Aging Studies to Unravel Underlying Mechanisms of Age-Related Dysfunction in Humans
Abstract
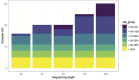
Aging is characterized by increased mortality, functional decline, and exponential increases in the incidence of diseases such as cancer, stroke, cardiovascular disease, neurological disease, respiratory disease, etc. Though the role of aging in these diseases is widely accepted and considered to be a common denominator, the underlying mechanisms are largely unknown. A significant age-related feature observed in many population cohorts is somatic mosaicism, the detectable accumulation of somatic mutations in multiple cell types and tissues, particularly those with high rates of cell turnover (e.g., skin, liver, and hematopoietic cells). Somatic mosaicism can lead to the development of cellular clones that expand with age in otherwise normal tissues. In the hematopoietic system, this phenomenon has generally been referred to as "clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential" (CHIP) when it applies to a subset of clones in which mutations in driver genes of hematologic malignancies are found. Other mechanisms of clonal hematopoiesis, including large chromosomal alterations, can also give rise to clonal expansion in the absence of conventional CHIP driver gene mutations. Both types of clonal hematopoiesis (CH) have been observed in studies of animal models and humans in association with altered immune responses, increased mortality, and disease risk. Studies in murine models have found that some of these clonal events are involved in abnormal inflammatory and metabolic changes, altered DNA damage repair and epigenetic changes. Studies in long-lived individuals also show the accumulation of somatic mutations, yet at this advanced age, carriership of somatic mutations is no longer associated with an increased risk of mortality. While it remains to be elucidated what factors modify this genotype-phenotype association, i.e., compensatory germline genetics, cellular context of the mutations, protective effects to diseases at exceptional age, it points out that the exceptionally long-lived are key to understand the phenotypic consequences of CHIP mutations. Assessment of the clinical significance of somatic mutations occurring in blood cell types for age-related outcomes in human populations of varied life and health span, environmental exposures, and germline genetic risk factors will be valuable in the development of personalized strategies tailored to specific somatic mutations for healthy aging.
Keywords: CHIP; aging; clonal hematopoiesis; longevity; somatic mutations.
Copyright © 2022 Walsh, Raghavachari, Kerr, Bick, Cummings, Druley, Dunbar, Genovese, Goodell, Jaiswal, Maciejewski, Natarajan, Shindyapina, Shuldiner, Van Den Akker and Vijg.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

