In vivo Pooled Screening: A Scalable Tool to Study the Complexity of Aging and Age-Related Disease
- PMID: 35822038
- PMCID: PMC9261400
- DOI: 10.3389/fragi.2021.714926
In vivo Pooled Screening: A Scalable Tool to Study the Complexity of Aging and Age-Related Disease
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: In Vivo Pooled Screening: A Scalable Tool to Study the Complexity of Aging and Age-Related Disease.Front Aging. 2021 Dec 3;2:804856. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2021.804856. eCollection 2021. Front Aging. 2021. PMID: 35822862 Free PMC article.
Abstract
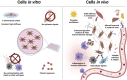
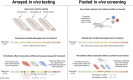
Biological aging, and the diseases of aging, occur in a complex in vivo environment, driven by multiple interacting processes. A convergence of recently developed technologies has enabled in vivo pooled screening: direct administration of a library of different perturbations to a living animal, with a subsequent readout that distinguishes the identity of each perturbation and its effect on individual cells within the animal. Such screens hold promise for efficiently applying functional genomics to aging processes in the full richness of the in vivo setting. In this review, we describe the technologies behind in vivo pooled screening, including a range of options for delivery, perturbation and readout methods, and outline their potential application to aging and age-related disease. We then suggest how in vivo pooled screening, together with emerging innovations in each of its technological underpinnings, could be extended to shed light on key open questions in aging biology, including the mechanisms and limits of epigenetic reprogramming and identifying cellular mediators of systemic signals in aging.
Keywords: aging models; animal models; barcoding; direct in vivo screening; gene therapy; in vivo; pooled screening; single cell sequencing.
Copyright © 2021 Borch Jensen and Marblestone.
Conflict of interest statement
MBJ was an employee and shareholder of Gordian Biotechnology. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Corrigendum: In Vivo Pooled Screening: A Scalable Tool to Study the Complexity of Aging and Age-Related Disease.Front Aging. 2021 Dec 3;2:804856. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2021.804856. eCollection 2021. Front Aging. 2021. PMID: 35822862 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping Cellular Reprogramming via Pooled Overexpression Screens with Paired Fitness and Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing Readout.Cell Syst. 2018 Nov 28;7(5):548-555.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2018.10.008. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Cell Syst. 2018. PMID: 30448000 Free PMC article.
-
Pooled genetic screens with image-based profiling.Mol Syst Biol. 2022 Nov;18(11):e10768. doi: 10.15252/msb.202110768. Mol Syst Biol. 2022. PMID: 36366905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene-nutrient interaction markedly influences yeast chronological lifespan.Exp Gerontol. 2016 Dec 15;86:113-123. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2016.04.012. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Exp Gerontol. 2016. PMID: 27125759 Free PMC article.
-
Pooled Genome-Scale CRISPR Screens in Single Cells.Annu Rev Genet. 2023 Nov 27;57:223-244. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-072920-013842. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Annu Rev Genet. 2023. PMID: 37562410 Review.
References
-
- Adamson B., Norman T. M., Jost M., Weissman J. S. (2018). Approaches to Maximize sgRNA-Barcode Coupling in Perturb-Seq Screens. bioRxiv. [Preprint]. 10.1101/298349 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

