A Novel Program to Improve Cognitive Function in Individuals With Dementia Using Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation (tACS) and Tutored Cognitive Exercises
- PMID: 35822057
- PMCID: PMC9261296
- DOI: 10.3389/fragi.2021.632545
A Novel Program to Improve Cognitive Function in Individuals With Dementia Using Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation (tACS) and Tutored Cognitive Exercises
Abstract
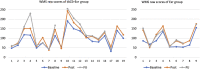
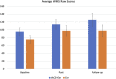
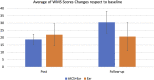
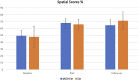
The effects of cognitive exercises on the healthy aging population is controversial. Transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) is considered a promising tool for modulating brain oscillation. Research is lacking on its long-lasting cognitive/therapeutic effect. This is the first pilot study to explore the effect of a regimen of cognitive exercises with and without tACS on older adults with dementia. The study groups were 28 individuals (age 56-83 years) enrolled into two groups: Exr Group, who received cognitive exercises only and the Exr + tACS Group who received tACS at 40 Hz simultaneously with cognitive exercises for a period of 4 consecutive weeks, 5 days/week, two 30 min-sessions/day; all the training sessions were tutored. The cognitive exercises were applied using the MindTriggers app. They were assessed at pre and post intervention and also one month after the end of trial (follow-up) with an independent assessment (WMS-IV) as the primary outcome measure. The results show significant cognitive improvement at post-intervention in both groups, while the Exr + tACS protocol lead to superior cognitive improvement at follow-up session. The most important outcomes of this study are: 1) The tutored repeated practice of the MindTriggers app exercises does significantly improve the cognitive functions of older adults with dementia and that that improvement lasts for at least one month after the end of the intervention, and 2) The application of tACS increases the positive effects of cognitive exercises with the positive effect lasting an even longer period of time than exercises alone; in other words we speculate that it may lead to long-term potentiation.
Keywords: alzheimer's; cognitive exercises; dementia; gamma band stimulation; mind triggers app; transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS); tutoring.
Copyright © 2021 Moussavi, Kimura, Kehler, de Oliveira Francisco and Lithgow.
Conflict of interest statement
ZM is the developer and owner of the MindTriggers app that has been used in this study. The apps small revenue is directed to her research budget for similar studies. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cognitive and Neuropathophysiological Outcomes of Gamma-tACS in Dementia: A Systematic Review.Neuropsychol Rev. 2024 Mar;34(1):338-361. doi: 10.1007/s11065-023-09589-0. Epub 2023 Mar 6. Neuropsychol Rev. 2024. PMID: 36877327 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive and Neuropsychiatric Effects of 40 Hz tACS Simultaneously with Cognitive Exercises for Dementia: A Randomized, Crossover, Double-Blind, Sham-Controlled Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Apr 19;61(4):757. doi: 10.3390/medicina61040757. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40283048 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) on cognitive function in older adults with dementia.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2020 Jul;2020:3649-3653. doi: 10.1109/EMBC44109.2020.9175903. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2020. PMID: 33018792
-
Tele-supervised home-based transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) for Alzheimer's disease: a pilot study.Front Hum Neurosci. 2023 Jun 2;17:1168673. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2023.1168673. eCollection 2023. Front Hum Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37333833 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroplastic effects of transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS): from mechanisms to clinical trials.Front Hum Neurosci. 2025 Mar 12;19:1548478. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2025.1548478. eCollection 2025. Front Hum Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40144589 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcranial Electrical Stimulation Offers the Possibility of Improving Teamwork Among Military Pilots: A Review.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jul 13;16:931265. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.931265. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35911997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cognitive and Neuropathophysiological Outcomes of Gamma-tACS in Dementia: A Systematic Review.Neuropsychol Rev. 2024 Mar;34(1):338-361. doi: 10.1007/s11065-023-09589-0. Epub 2023 Mar 6. Neuropsychol Rev. 2024. PMID: 36877327 Free PMC article.
-
Improving working memory by electrical stimulation and cross-frequency coupling.Mol Brain. 2024 Oct 1;17(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s13041-024-01142-1. Mol Brain. 2024. PMID: 39354549 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal gamma-band entrainment of visual cortex.Hum Brain Mapp. 2024 Jul 15;45(10):e26775. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26775. Hum Brain Mapp. 2024. PMID: 38970249 Free PMC article.
-
A Focused Review of Gamma Neuromodulation as a Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer's Spectrum Disorders.J Psychiatr Brain Sci. 2024;9(1):e240001. doi: 10.20900/jpbs.20240001. Epub 2024 Feb 28. J Psychiatr Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38550308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baltes P., Baltes M. (1990). “Psychological perspectives on successful aging: the model of selective optimization with compensation,” in Successful aging: Perspectives from the behavioral Sciences (European network on Longitudinal studies on individual Development. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press, 1–34.
-
- Boudreaus E. O. (2010). Individual differences and memory aging Concerns of older adults. Baton Rouge, LA: Louisiana State University.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

