Improving yield of a recombinant biologic in a Brassica hairy root manufacturing process
- PMID: 35822204
- PMCID: PMC9543041
- DOI: 10.1002/bit.28178
Improving yield of a recombinant biologic in a Brassica hairy root manufacturing process
Abstract
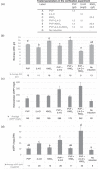
Hairy root systems have proven to be a viable alternative for recombinant protein production. For recalcitrant proteins, maximizing the productivity of hairy root cultures is essential. The aim of this study was to optimize a Brassica rapa rapa hairy root process for secretion of alpha- l-iduronidase (IDUA), a biologic of medical value. The process was first optimized with hairy roots expressing eGFP. For the biomass optimization, the highest biomass yields were achieved in modified Gamborg B5 culture medium. For the secretion induction, the optimized secretion media was obtained with additives (1.5 g/l PVP + 1 mg/l 2,4- d + 20.5 g/l KNO3 ) resulting in 3.4 fold eGFP secretion when compared to the non-induced control. These optimized conditions were applied to the IDUA-expressing hairy root clone, confirming that the highest yields of secreted IDUA occurred when using the defined additive combination. The functionality of the IDUA protein, secreted and intracellular, was confirmed with an enzymatic activity assay. A > 150-fold increase of the IDUA activity was observed using an optimized secretion medium, compared with a non-induced medium. We have proven that our B. rapa rapa hairy root system can be harnessed to secrete recalcitrant proteins, illustrating the high potential of hairy roots in plant molecular farming.
Keywords: alpha-l-iduronidase; eGFP; hairy root; plant molecular farming; recombinant protein; secretion.
© 2022 The Authors. Biotechnology and Bioengineering published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Florian Cardon, Camille Lemasson, and Marina Guillet are employed by the company Samabriva SA. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Molecular farming in tobacco hairy roots by triggering the secretion of a pharmaceutical antibody.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2014 Feb;111(2):336-46. doi: 10.1002/bit.25113. Epub 2013 Sep 24. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2014. PMID: 24030771
-
Brassica rapa hairy root based expression system leads to the production of highly homogenous and reproducible profiles of recombinant human alpha-L-iduronidase.Plant Biotechnol J. 2019 Feb;17(2):505-516. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12994. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Plant Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 30058762 Free PMC article.
-
MALDI-TOF characterization of hGH1 produced by hairy root cultures of Brassica oleracea var. italica grown in an airlift with mesh bioreactor.Biotechnol Prog. 2014 Jan-Feb;30(1):161-71. doi: 10.1002/btpr.1829. Epub 2013 Oct 23. Biotechnol Prog. 2014. PMID: 24124083
-
Production and metabolic engineering of bioactive substances in plant hairy root culture.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011 May;90(4):1229-39. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3228-0. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21468707 Review.
-
Large-scale production of hairy root.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2004;91:75-103. doi: 10.1007/b94206. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2004. PMID: 15453193 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Progress on Vaccines Produced in Transgenic Plants.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Nov 3;10(11):1861. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10111861. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36366370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Untapped Potential of Hairy Root Cultures and Their Multiple Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 26;25(23):12682. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312682. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684394 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alvarez, M. A. (2014). The antibody 14D9 as an experimental model for molecular farming, Plant biotechnology for health (pp. 111–131). Springer.
-
- Shelton A. M., Zhao J.‐Z., Roush RT. (2002). Economic, ecological, food safety, and social consequences of the deployment of Bt transgenic plants. Annual Review of Entomology, 47, 845–881. - PubMed
-
- Cardon, F. , Pallisse, R. , Bardor, M. , Caron, A. , Vanier, J. , Ele Ekouna, J. P. , Lerouge, P. , Boitel‐Conti, M. , & Guillet, M. (2019). Brassica rapa hairy root based expression system leads to the production of highly homogenous and reproducible profiles of recombinant human alpha‐L‐iduronidase. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 17, 505–516. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dehdashti, S. M. , Acharjee, S. , Nomani, A. , & Deka, M. (2020). Production of pharmaceutical active recombinant globular adiponectin as a secretory protein in Withania somnifera hairy root culture. Journal of Biotechnology, 323, 302–312. - PubMed
-
- Drake, P. M. , Barbi, T. , Sexton, A. , McGowan, E. , Stadlmann, J. , Navarre, C. , Paul, M. J. , & Ma, J. K.‐C. (2009). Development of rhizosecretion as a production system for recombinant proteins from hydroponic cultivated tobacco. FASEB Journal, 23, 3581–3589. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

