The symmetry of the left and right tibial plateau: a comparison of 200 tibial plateaus
- PMID: 35829733
- PMCID: PMC9925587
- DOI: 10.1007/s00068-022-02043-5
The symmetry of the left and right tibial plateau: a comparison of 200 tibial plateaus
Abstract
Purpose: This study aims to investigate the symmetry of the left and right tibial plateau in young healthy individuals to determine whether left-right mirroring can be reliably used to optimize preoperative 3D virtual planning for patients with tibial plateau fractures.
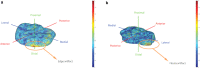
Methods: One hundred healthy subjects, without previous knee surgery, severe knee trauma, or signs of osteoarthritis were included for a previous dynamic imaging study of the knee. The subjects underwent a CT scan, scanning the left and right knee with a slice thickness of 0.8 mm. 3D surface models of the femur, patella, and tibia were created using a convolutional neural network. The 3D models of the left and right tibias were exported to MATLAB © and the tibias were mirrored. The mirrored tibias were superimposed on the contralateral tibia using a coherent point drift surface matching algorithm. Correspondence points on both surfaces were established, the mean root squared distance was calculated and visualized in a boxplot and heatmaps.
Results: The overall mean difference between correspondence points on the left and right tibial plateau is 0.6276 ± 0.0343 mm. The greatest differences between correspondence points were seen around two specific surfaces on the outside of the tibial plateau; where the distal tibia was cut 15 mm below the tibial plateau and around the tibiofibular joint.
Conclusions: The differences between the left and right tibial plateau are small and therefore, we can be confident that the mirrored contralateral, unfractured, tibial plateau can be used as a template for 3D virtual preoperative planning for young patients without previous damage to the knee.
Keywords: 3D virtual planning; Surgical planning; Symmetry; Tibial plateau; Tibial plateau fractures.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Each author certifies that there are no funding or commercial associations (consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc.) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article related to the author or any immediate family members.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

