The Predictive Value of CHA2DS2-VASc Score on Residual Syntax Score in Patients With ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 35830076
- PMCID: PMC9438551
- DOI: 10.36660/abc.20210670
The Predictive Value of CHA2DS2-VASc Score on Residual Syntax Score in Patients With ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Erratum in
-
Errata.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2023 Jul 24;120(7):e20230356. doi: 10.36660/abc.20230356. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37493652 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese.
Abstract
Background: The CHA2DS2-VASc score is associated with adverse clinical outcomes in patients with cardiovascular disease. The residual Syntax score (rSS) is a scoring tool which has prognostic value in patients with ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).
Objectives: Our aim in this study is to investigate the predictive value of the CHA2DS2-VASc score on rSS in STEMI patients.
Methods: A total of 688 consecutive patients with STEMI undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention were evaluated. Baseline demographic and clinical variables besides the CHA2DS2-VASc score were assessed. The patients were divided into two groups; patients with rSS of 8 or below as group 1 (509 patients) and more than 8 as group 2 (179 patients). A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
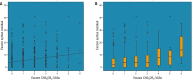
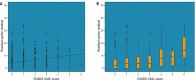
Results: The CHA2DS2-VASc score was higher in group 2 [1 (0-2); 1 (1-3), p<0.001] compared to group 1. The incidence of hypertension [151 (29.7%); 73 (40.8%), p=0.006], patients ≥75 years [18 (3.5%); 21 (11.7%), p<0.001], diabetes mellitus [85 (16.7%); 50 (27.9%), p=0.001] and vascular disease [12 (2.4%); 11 (6.1%), p=0.029] were higher in group 2. In multivariate logistic regression analysis, the CHA2DS2-VASc score (OR=1.355; 95%CI=1.171-1.568; p<0.001), age ≥75 years [OR=3.218; 95%CI=1.645-6.295; p=0.001] and diabetes mellitus [OR=1.670; 95%CI=1.091-2.557; p=0.018] were independent predictors of high rSS. The receiver-operating characteristic curve analysis demonstrated that the CHA2DS2-VASc score had good predictive value for high rSS with a cut-off value of 1.5 (area under curve (AUC): 0.611, 95% confidence interval (CI):0.562-0.659, p<0.001).
Conclusions: The CHA2DS2-VASc score has a predictive value on rSS in patients with STEMI. The CHA2DS2-VASc score was also an independent predictor of higher rSS.
Fundamento: O escore CHA2DS2-VASc está associado a desfechos clínicos adversos em pacientes com doença cardiovascular. O escore Syntax residual (residual Syntax score — rSS) é uma ferramenta de pontuação que tem valor prognóstico em pacientes com infarto agudo do miocárdio com supradesnivelamento do segmento ST (IAMCSST).
Objetivos: Este estudo objetivou investigar o valor preditivo do escore CHA2DS2-VASc para o rSS em pacientes com IAMCSST.
Métodos: Foram avaliados 688 pacientes consecutivos com IAMCSST submetidos à intervenção coronária percutânea. Além do escore CHA2DS2-VASc, variáveis demográficas e clínicas de referência foram analisadas. Os pacientes foram divididos em dois grupos: grupo 1 – indivíduos com rSS até 8 (509 pacientes); grupo 2 – aqueles com rSS acima de 8 (179 pacientes). Valores p<0,05 foram considerados estatisticamente significativos.
Resultados: O escore CHA2DS2-VASc foi maior no grupo 2 [1 (0–2); 1 (1–3), p<0,001] comparado ao grupo 1. A incidência de hipertensão [151 (29,7%); 73 (40,8%), p=0,006], idade ≥75 anos [18 (3,5%); 21 (11,7%), p<0,001], diabetes mellitus [85 (16,7%); 50 (27,9%), p=0,001] e doença vascular [12 (2,4%); 11 (6,1%), p=0,029] foi maior no grupo 2. Na análise de regressão logística multivariada, o escore CHA2DS2-VASc (odds ratio — OR=1,355; intervalo de confiança de 95% — IC95%=1,171–1,568; p<0,001), idade ≥75 anos [OR=3,218; IC95%=1,645–6,295; p=0,001] e diabetes mellitus [OR=1,670; IC95%=1,091–2,557; p=0,018] foram preditores independentes de rSS elevado. A análise da curva receiver-operating characteristic demonstrou o bom valor preditivo do escore CHA2DS2-VASc para rSS elevado com valor de corte de 1,5 (área sob a curva/area under the curve — AUC= 0,611, IC95%=0,562–0,659, p<0,001).
Conclusões: O escore CHA2DS2-VASc tem valor preditivo para rSS em pacientes com IAMCSST. Além disso, o escore CHA2DS2-VASc foi um preditor independente de rSS mais alto.
Conflict of interest statement
Potencial conflito de interesse
Não há conflito com o presente artigo.
Figures
Comment in
-
Atherosclerotic Burden is the Highway to Cardiovascular Events.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022 Sep;119(3):400-401. doi: 10.36660/abc.20220554. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 36074373 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese. No abstract available.
References
-
- Généreux P, Palmerini T, Caixeta A, Rosner G, Green P, Dressler O, et al. Quantification and Impact of Untreated Coronary Artery Disease After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: The Residual SYNTAX (Synergy Between PCI with Taxus and Cardiac Surgery) Score. 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.03.010J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;59(24):2165–2174. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Perk J, De Backer G, Gohlke H, Graham I, Reiner Z, Verschuren M, et al. European Guidelines on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (version 2012). The Fifth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (constituted by representatives of Nine Societies and by Invited Experts) Eur Heart J. 2012;33(13):1635–1701. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs092. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ford ES, Giles WH, Mokdad AH. The Distribution of 10-Year Risk for Coronary Heart Disease Among US Adults: Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III. 10.1016/j.jacc.2003.11.061J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43(10):1791–1796. - PubMed
-
- Eberly LE, Neaton JD, Thomas AJ, Yu D, Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial Research Group Multiple-Stage Screening and Mortality in the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial. 10.1191/1740774504cn018oaClin Trials. 2004;1(2):148–161. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources