Catheter Ablation is Superior to Antiarrhythmic Drugs as First-Line Treatment for Atrial Fibrillation: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35830118
- PMCID: PMC9352118
- DOI: 10.36660/abc.20210477
Catheter Ablation is Superior to Antiarrhythmic Drugs as First-Line Treatment for Atrial Fibrillation: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Catheter ablation is a well-established therapy for rhythm control in patients who are refractory or intolerant to anti-arrhythmic drugs (AAD). Less is known about the efficacy of catheter ablation compared with AAD as a first-line strategy for rhythm control in atrial fibrillation (AF).
Objectives: We aimed to perform a systematic review and meta-analysis of catheter ablation vs. AAD in patients naïve to prior rhythm control therapies.
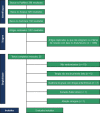
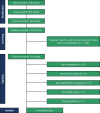
Methods: PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane databases were searched for randomized controlled trials that compared catheter ablation to AAD for initial rhythm control in symptomatic AF and reported the outcomes of (1) recurrent atrial tachyarrhythmias (ATs); (2) symptomatic AF; (3) hospitalizations; and (4) symptomatic bradycardia. Heterogeneity was examined with I2statistics. P values of < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results: We included five trials with 994 patients, of whom 502 (50.5%) underwent catheter ablation. Mean follow-up ranged from one to five years. Recurrences of AT (OR 0.36; 95% CI 0.25-0.52; p<0.001) and symptomatic AF (OR 0.32; 95% CI 0.18-0.57; p<0.001), and hospitalizations (OR 0.25; 95% CI 0.15-0.42; p<0.001) were significantly less frequent in patients treated with catheter ablation compared with AAD. Symptomatic bradycardia was not significantly different between groups (OR 0.55; 95% CI 0.18-1.65; p=0.28). Significant pericardial effusions or tamponade occurred in eight of 464 (1.7%) patients in the catheter ablation group.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that catheter ablation has superior efficacy to AAD as an initial rhythm control strategy in patients with symptomatic AF.
Fundamento: A ablação por cateter é uma terapia bem estabelecida para controle do ritmo cardíaco em pacientes refratários ou intolerantes a drogas antiarrítmicas (DAA). Porém, a eficácia desse procedimento comparada à de DAA como estratégia de primeira linha no controle do ritmo cardíaco na fibrilação atrial é menos conhecida.
Objetivos: Conduzir uma revisão sistemática e metanálise da ablação por cateter vs. DAA em pacientes sem nenhum tratamento prévio para controle do ritmo.
Métodos: Buscamos, nos bancos de dados do PubMed, EMBASE, e Cochrane, ensaios randomizados controlados que compararam ablação por cateter com DAA para controle do ritmo cardíaco em pacientes com FA sintomática e descreveram os seguintes desfechos: (1) recorrência de taquiarritmia atrial (TA); (2) FA sintomática; (3) internações hospitalares; e (4) bradicardia sintomática. A heterogeneidade foi avaliada por estatística I2. Valores de p menores que 0,05 foram considerados estatisticamente significativos.
Resultados: Incluímos cinco ensaios com 994 pacientes, dos quais 502 (50,5%) foram submetidos à ablação por cateter. O período médio de acompanhamento foi de um a cinco anos. Recorrências de TA (OR 0,36; IC95% 0,25-0,52; p<0,001) e de FA sintomática (OR 0,32; IC95% 0,18-0,57; p<0,001), e internações hospitalares (OR 0,25; IC95% 0,15-0,42; p<0,001) foram menos frequentes nos pacientes tratados com ablação por cateter que naqueles tratados com DAA. Bradicardia sintomática não foi diferente entre os grupos (OR 0,55; IC95% 0,18-1,65; p=0,28). Derrame ou tamponamento pericárdico significativo ocorreu em oito dos 464 (1,7%) pacientes no grupo submetido à ablação.
Conclusão: Esses achados sugerem maior eficácia da ablação por cateter que das DAA como estratégia inicial de controle do ritmo cardíaco em pacientes com DA sintomática.
Conflict of interest statement
Potencial conflito de interesse
Não há conflito com o presente artigo
Figures








Comment in
-
Catheter Ablation as First-Line Therapy in the Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation - Should We Always Indicate it?Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022 Jul;119(1):95-96. doi: 10.36660/abc.20220362. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35830105 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese. No abstract available.
References
-
- Virani SS, Alonso A, Benjamin EJ, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2020 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;141(9):139-596. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000757. - PubMed
-
- Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomström-Lundqvist C, et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation Developed in Collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the Special Contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(5):373-498. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa612. - PubMed
-
- January CT, Wann LS, Calkins H, Chen LY, Cigarroa JE, Cleveland JC Jr, et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS Focused Update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society in Collaboration with the Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Circulation. 2019;140(2):125-51. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000665. - PubMed
-
- Marrouche NF, Brachmann J, Andresen D, Siebels J, Boersma L, Jordaens L, et al. Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation with Heart Failure. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(5):417-27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1707855. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

