The secret life of insect-associated microbes and how they shape insect-plant interactions
- PMID: 35830517
- PMCID: PMC9409087
- DOI: 10.1093/femsec/fiac083
The secret life of insect-associated microbes and how they shape insect-plant interactions
Erratum in
-
Correction to: The secret life of insect-associated microbes and how they shape insect-plant interactions.FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2022 Oct 10;98(10):fiac116. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiac116. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2022. PMID: 36215208 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Insects are associated with a plethora of different microbes of which we are only starting to understand their role in shaping insect-plant interactions. Besides directly benefitting from symbiotic microbial metabolism, insects obtain and transmit microbes within their environment, making them ideal vectors and potential beneficiaries of plant diseases and microbes that alter plant defenses. To prevent damage, plants elicit stress-specific defenses to ward off insects and their microbiota. However, both insects and microbes harbor a wealth of adaptations that allow them to circumvent effective plant defense activation. In the past decades, it has become apparent that the enormous diversity and metabolic potential of insect-associated microbes may play a far more important role in shaping insect-plant interactions than previously anticipated. The latter may have implications for the development of sustainable pest control strategies. Therefore, this review sheds light on the current knowledge on multitrophic insect-microbe-plant interactions in a rapidly expanding field of research.
Keywords: insects; insect–microbe–plant interactions; microbiota; pathogens; plant defenses; symbionts.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of FEMS.
Figures
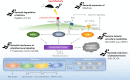
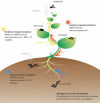
Similar articles
-
Tritrophic Interactions: Microbe-Mediated Plant Effects on Insect Herbivores.Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2017 Aug 4;55:313-331. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-080516-035319. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2017. PMID: 28590879 Review.
-
Evaluating insect-microbiomes at the plant-insect interface.J Chem Ecol. 2014 Jul;40(7):836-47. doi: 10.1007/s10886-014-0475-4. Epub 2014 Jul 23. J Chem Ecol. 2014. PMID: 25052911 Review.
-
Evolutionary Ecology of Multitrophic Interactions between Plants, Insect Herbivores and Entomopathogens.J Chem Ecol. 2017 Jun;43(6):586-598. doi: 10.1007/s10886-017-0850-z. Epub 2017 May 19. J Chem Ecol. 2017. PMID: 28526946 Review.
-
Three-way interaction among plants, bacteria, and coleopteran insects.Planta. 2016 Aug;244(2):313-32. doi: 10.1007/s00425-016-2543-1. Epub 2016 May 11. Planta. 2016. PMID: 27170360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exchange of Microbiomes in Plant-Insect Herbivore Interactions.mBio. 2023 Apr 25;14(2):e0321022. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03210-22. Epub 2023 Mar 7. mBio. 2023. PMID: 36880763 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamics of bacterial communities across developmental stages of the litchi stink bug, Tessaratoma javanica.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 8;15(1):29106. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00598-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40781242 Free PMC article.
-
Rickettsia transmission from whitefly to plants benefits herbivore insects but is detrimental to fungal and viral pathogens.mBio. 2024 Mar 13;15(3):e0244823. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02448-23. Epub 2024 Feb 5. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38315036 Free PMC article.
-
Arsenophonus: A Double-Edged Sword of Aphid Defense against Parasitoids.Insects. 2023 Sep 13;14(9):763. doi: 10.3390/insects14090763. Insects. 2023. PMID: 37754731 Free PMC article.
-
Anna Karenina as a promoter of microbial diversity in the cosmopolitan agricultural pest Zeugodacus cucurbitae (Diptera, Tephritidae).PLoS One. 2024 Apr 3;19(4):e0300875. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300875. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38568989 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiome and plant cell transformation trigger insect gall induction in cassava.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Nov 29;14:1237966. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1237966. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 38126017 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali JG, Agrawal AA. Specialist versus generalist insect herbivores and plant defense. Trends Plant Sci. 2012;17:293–302. - PubMed
-
- Ali S, Charles TC, Glick BR. Endophytic Phytohormones and Their Role in Plant Growth Promotion. Functional Importance of the Plant Microbiome. Doty S (ed.), Cham: Springer, 2017, 89–105.
-
- Almeida RPP, Blua MJ, Lopes JRSet al. . Vector transmission of Xylellafastidiosa: applying fundamental knowledge to generate disease management strategies. Ann Entomol Soc Am. 2005;98:775–86.
-
- Ammar ED, Correa V, Hogenhout Set al. . Immunofluorescence localization and ultrastructure of Stewart's wilt disease bacterium Pantoea stewartii in maize leaves and in its flea beetle vector Chaetocnema pulicaria (Coleoptera: chrysomelidae). J Microscopy Ultrastruct. 2014;2:28–33.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

