GATA transcription factor WC2 regulates the biosynthesis of astaxanthin in yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous
- PMID: 35830570
- PMCID: PMC9518987
- DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.14115
GATA transcription factor WC2 regulates the biosynthesis of astaxanthin in yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous
Abstract
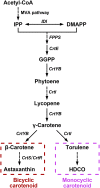
Astaxanthin is a type of carotenoid widely used as powerful antioxidant and colourant in aquaculture and the poultry industry. Production of astaxanthin by yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous has attracted increasing attention due to high cell density and low requirements of water and land compared to photoautotrophic algae. Currently, the regulatory mechanisms of astaxanthin synthesis in X. dendrorhous remain obscure. In this study, we obtained a yellow X. dendrorhous mutant by Atmospheric and Room Temperature Plasma (ARTP) mutagenesis and sequenced its genome. We then identified a putative GATA transcription factor, white collar 2 (XdWC2), from the comparative genome data and verified that disruption of the XdWC2 gene resulted in a similar carotenoid profile to that of the ARTP mutant. Furthermore, transcriptomic analysis and yeast one-hybrid (Y1H) assay showed that XdWC2 regulated the expression of phytoene desaturase gene CrtI and astaxanthin synthase gene CrtS. The yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) assay demonstrated that XdWC2 interacted with white collar 1 (XdWC1) forming a heterodimer WC complex (WCC) to regulate the expression of CrtI and CrtS. Increase of the transcriptional levels of XdWC2 or CrtS in the wild-type strain did not largely modify the carotenoid profile, indicating translational and/or post-translational regulations involved in the biosynthesis of astaxanthin. Overexpression of CrtI in both the wild-type strain and the XdWC2-disrupted strain apparently improved the production of monocyclic carotenoid 3-hydroxy-3', 4'-didehydro-β, ψ-carotene-4-one (HDCO) rather than β-carotene and astaxanthin. The regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis by XdWC2 presented here provides the foundation for further understanding the global regulation of astaxanthin biosynthesis and guides the construction of astaxanthin over-producing strains.
© 2022 The Authors. Microbial Biotechnology published by Society for Applied Microbiology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Metabolic engineering of the astaxanthin-biosynthetic pathway of Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous.FEMS Yeast Res. 2003 Dec;4(3):221-31. doi: 10.1016/S1567-1356(03)00158-2. FEMS Yeast Res. 2003. PMID: 14654426 Review.
-
Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for astaxanthin production and oxidative stress tolerance.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009 Nov;75(22):7205-11. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01249-09. Epub 2009 Oct 2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19801484 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic engineering of the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway in the yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous (Phaffia rhodozyma).Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003 Jul;69(7):3728-38. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.7.3728-3738.2003. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12839738 Free PMC article.
-
The crtS gene of Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous encodes a novel cytochrome-P450 hydroxylase involved in the conversion of beta-carotene into astaxanthin and other xanthophylls.Fungal Genet Biol. 2006 Apr;43(4):261-72. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2005.12.004. Epub 2006 Feb 7. Fungal Genet Biol. 2006. PMID: 16455271
-
Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous for the industrial production of astaxanthin.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010 Oct;88(3):645-58. doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2814-x. Epub 2010 Aug 14. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20711573 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of Atmospheric and Room-Temperature Plasma (ARTP) to Microbial Breeding.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Aug 4;45(8):6466-6484. doi: 10.3390/cimb45080408. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37623227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances and trends for astaxanthin synthesis in Phaffia rhodozyma.Microb Cell Fact. 2025 May 6;24(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12934-025-02704-1. Microb Cell Fact. 2025. PMID: 40329361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Omics-driven onboarding of the carotenoid producing red yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous CBS 6938.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Dec 28;108(1):547. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13379-w. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39731599 Free PMC article.
-
The photoinduced β-carotene synthesis in Blakeslea trispora is dependent on WC-2A.Front Microbiol. 2025 Mar 25;16:1554367. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1554367. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40201436 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Álvarez, V. , Rodríguez‐Sáiz, M. , de la Fuente, J.L. , Gudiña, E.J. , Godio, R.P. , Martín, J.F. et al. (2006) The crtS gene of Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous encodes a novel cytochrome‐P450 hydroxylase involved in the conversion of β‐carotene into astaxanthin and other xanthophylls. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 43, 261–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

