siRNA-based nanotherapeutics as emerging modalities for immune-mediated diseases: A preliminary review
- PMID: 35830711
- PMCID: PMC9543380
- DOI: 10.1002/cbin.11841
siRNA-based nanotherapeutics as emerging modalities for immune-mediated diseases: A preliminary review
Abstract
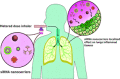
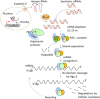
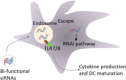
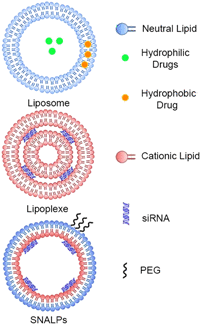
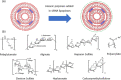
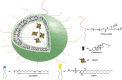
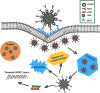
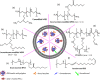
Immune-mediated diseases (IMDs) are chronic conditions that have an immune-mediated etiology. Clinically, these diseases appear to be unrelated, but pathogenic pathways have been shown to connect them. While inflammation is a common occurrence in the body, it may either stimulate a favorable immune response to protect against harmful signals or cause illness by damaging cells and tissues. Nanomedicine has tremendous promise for regulating inflammation and treating IMIDs. Various nanoparticles coated with nanotherapeutics have been recently fabricated for effective targeted delivery to inflammatory tissues. RNA interference (RNAi) offers a tremendous genetic approach, particularly if traditional treatments are ineffective against IMDs. In cells, several signaling pathways can be suppressed by using RNAi, which blocks the expression of particular messenger RNAs. Using this molecular approach, the undesirable effects of anti-inflammatory medications can be reduced. Still, there are many problems with using short-interfering RNAs (siRNAs) to treat IMDs, including poor localization of the siRNAs in target tissues, unstable gene expression, and quick removal from the blood. Nanotherapeutics have been widely used in designing siRNA-based carriers because of the restricted therapy options for IMIDs. In this review, we have discussed recent trends in the fabrication of siRNA nanodelivery systems, including lipid-based siRNA nanocarriers, liposomes, and cationic lipids, stable nucleic acid-lipid particles, polymeric-based siRNA nanocarriers, polyethylenimine (PEI)-based nanosystems, chitosan-based nanoformulations, inorganic material-based siRNA nanocarriers, and hybrid-based delivery systems. We have also introduced novel siRNA-based nanocarriers to control IMIDs, such as pulmonary inflammation, psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, etc. This study will pave the way for new avenues of research into the diagnosis and treatment of IMDs.
Keywords: autoimmunity; drug delivery; inflammation; nanotechnology; nanotherapeutics; siRNA.
© 2022 The Authors. Cell Biology International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of International Federation of Cell Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The emerging potential of siRNA nanotherapeutics in treatment of arthritis.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023 Sep;18(5):100845. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2023.100845. Epub 2023 Sep 16. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023. PMID: 37881798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Budding Alliance of Nanotechnology in RNA Interference Therapeutics.Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(23):2632-2643. doi: 10.2174/1381612824666180807113948. Curr Pharm Des. 2018. PMID: 30084328 Review.
-
Nanotherapeutics for the Treatment of Cancer and Arthritis.Curr Drug Metab. 2019;20(6):430-445. doi: 10.2174/1389200220666181127102720. Curr Drug Metab. 2019. PMID: 30479211 Review.
-
Lipid-based nanoparticles for siRNA delivery in cancer therapy: paradigms and challenges.Acc Chem Res. 2012 Jul 17;45(7):1163-71. doi: 10.1021/ar300048p. Epub 2012 May 8. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 22568781
-
Lipidoid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles loaded with TNF siRNA suppress inflammation after intra-articular administration in a murine experimental arthritis model.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2019 Sep;142:38-48. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2019.06.009. Epub 2019 Jun 11. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2019. PMID: 31199978
Cited by
-
Nanotechnology-Driven Drug Delivery Systems for Lung Cancer: Computational Advances and Clinical Perspectives.Thorac Cancer. 2025 Jul;16(14):e70134. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.70134. Thorac Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40682256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticles targeting monocytes and macrophages as diagnostic and therapeutic tools for autoimmune diseases.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 7;9(9):e19861. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19861. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37810138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomedicine in Neuroprotection, Neuroregeneration, and Blood-Brain Barrier Modulation: A Narrative Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Aug 24;60(9):1384. doi: 10.3390/medicina60091384. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39336425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The association between ADAM12 gene polymorphisms and osteoarthritis: an updated meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Mar 1;18(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03626-7. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 36855121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angle-controllable RNA tiles for programable array assembly and RNA sensing.Nat Commun. 2025 Apr 19;16(1):3728. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58938-5. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40253384 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abd Ellah, N. H. , Khalil, I. A. , & Harashima, H. (2021). Non‐viral gene delivery. The ADME Encyclopedia: A Comprehensive Guide on Biopharmacy and Pharmacokinetics, 1, 10.
-
- Akhilesh, A. , Uniyal, A. , Gadepalli, A. , Tiwari, V. , Allani, M. , Chouhan, D. , Ummadisetty, O. , Verma, N. , & Tiwari, V. (2022). Unlocking the potential of TRPV1 based siRNA therapeutics for the treatment of chemotherapy‐induced neuropathic pain. Life Sciences, 288, 120187. - PubMed
-
- Alabi, C. , Vegas, A. , & Anderson, D. (2012). Attacking the genome: Emerging siRNA nanocarriers from concept to clinic. Current Opinion in Pharmacology, 12, 427–433. - PubMed
-
- Aldayel, A. M. , O'Mary, H. L. , Valdes, S. A. , Li, X. , Thakkar, S. G. , Mustafa, B. E. , & Cui, Z. (2018). Lipid nanoparticles with minimum burst release of TNF‐α siRNA show strong activity against rheumatoid arthritis unresponsive to methotrexate. Journal of Controlled Release, 283, 280–289. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

