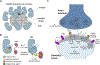
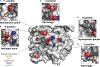
CaMKII binds both substrates and activators at the active site
- PMID: 35830796
- PMCID: PMC9336311
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111064
CaMKII binds both substrates and activators at the active site
Abstract
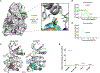
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) is a signaling protein required for long-term memory. When activated by Ca2+/CaM, it sustains activity even after the Ca2+ dissipates. In addition to the well-known autophosphorylation-mediated mechanism, interaction with specific binding partners also persistently activates CaMKII. A long-standing model invokes two distinct S and T sites. If an interactor binds at the T-site, then it will preclude autoinhibition and allow substrates to be phosphorylated at the S site. Here, we specifically test this model with X-ray crystallography, molecular dynamics simulations, and biochemistry. Our data are inconsistent with this model. Co-crystal structures of four different activators or substrates show that they all bind to a single continuous site across the kinase domain. We propose a mechanistic model where persistent CaMKII activity is facilitated by high-affinity binding partners that kinetically compete with autoinhibition by the regulatory segment to allow substrate phosphorylation.
Keywords: AMPA-type glutamate receptor; CP: Molecular biology; Ca(2+)/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II; LTP; NMDA-type glutamate receptor; Tiam1; X-ray crystallography.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests Y.H. received research funds from Fujitsu Laboratories and Dwango.
Figures
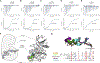
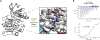

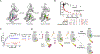
References
-
- Barker SC, Kassel DB, Weigl D, Huang X, Luther MA, and Knight WB (1995). Characterization of pp60c-src tyrosine kinase activities using a continuous assay: autoactivation of the enzyme is an intermolecular autophosphorylation process. Biochemistry 34, 14843–14851. 10.1021/bi00045a027. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barria A, Derkach V, and Soderling T (1997a). Identification of the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II regulatory phosphorylation site in the alpha-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate-type glutamate receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 32727–32730. 10.1074/jbc.272.52.32727. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

