Structure of the MRAS-SHOC2-PP1C phosphatase complex
- PMID: 35830882
- PMCID: PMC9452295
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1
Structure of the MRAS-SHOC2-PP1C phosphatase complex
Abstract
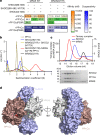
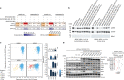
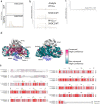
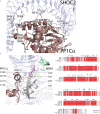
RAS-MAPK signalling is fundamental for cell proliferation and is altered in most human cancers1-3. However, our mechanistic understanding of how RAS signals through RAF is still incomplete. Although studies revealed snapshots for autoinhibited and active RAF-MEK1-14-3-3 complexes4, the intermediate steps that lead to RAF activation remain unclear. The MRAS-SHOC2-PP1C holophosphatase dephosphorylates RAF at serine 259, resulting in the partial displacement of 14-3-3 and RAF-RAS association3,5,6. MRAS, SHOC2 and PP1C are mutated in rasopathies-developmental syndromes caused by aberrant MAPK pathway activation6-14-and SHOC2 itself has emerged as potential target in receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)-RAS-driven tumours15-18. Despite its importance, structural understanding of the SHOC2 holophosphatase is lacking. Here we determine, using X-ray crystallography, the structure of the MRAS-SHOC2-PP1C complex. SHOC2 bridges PP1C and MRAS through its concave surface and enables reciprocal interactions between all three subunits. Biophysical characterization indicates a cooperative assembly driven by the MRAS GTP-bound active state, an observation that is extendible to other RAS isoforms. Our findings support the concept of a RAS-driven and multi-molecular model for RAF activation in which individual RAS-GTP molecules recruit RAF-14-3-3 and SHOC2-PP1C to produce downstream pathway activation. Importantly, we find that rasopathy and cancer mutations reside at protein-protein interfaces within the holophosphatase, resulting in enhanced affinities and function. Collectively, our findings shed light on a fundamental mechanism of RAS biology and on mechanisms of clinically observed enhanced RAS-MAPK signalling, therefore providing the structural basis for therapeutic interventions.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Z.J.H., A.D., J.V., D.E., M.B., S.K., K.A.P., F.M., H.G., G.K., S.M., C.V.-V., K.S.B., G.G.G., S.-M.M., T.S., K.C., L.T., C.R.T. and D.A.K. are employees and shareholders of Novartis Pharma. M.F. is a former employee of Novartis. M.J.E. receives funding from Novartis Pharma.
Figures







Comment in
-
Structural keys unlock RAS-MAPK cellular signalling pathway.Nature. 2022 Sep;609(7926):248-249. doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-02189-7. Nature. 2022. PMID: 35970881 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lavoie H, Therrien M. Regulation of RAF protein kinases in ERK signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015;16:281–298. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez-Viciana P, et al. A phosphatase holoenzyme comprised of Shoc2/Sur8 and the catalytic subunit of PP1 functions as an M-Ras effector to modulate Raf activity. Mol. Cell. 2006;22:217–230. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

