Predictors of tympanostomy tube extrusion time in otitis media with effusion
- PMID: 35830986
- PMCID: PMC9749685
- DOI: 10.15537/smj.2022.43.7.20220323
Predictors of tympanostomy tube extrusion time in otitis media with effusion
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the impact and predictors of tympanostomy tube (TT) extrusion.
Methods: A retrospective study on 258 ears underwent TT insertion during 2016-2018 at King Abdullah Specialized Children's Hospital, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Patients were followed for 36-48 months postoperatively to detect the recurrence rate. The sample was divided into 2 groups based on extrusion time and were compared to determine the predictors of TT extrusion.
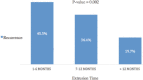
Results: Otitis media with effusion (OME) recurrence after TT insertion was detected in 28.7%. A shorter TT extrusion time was associated with a higher recurrence (p=0.002). Small TTs increased the probability of early TT extrusion (odds ratio = 5.144; 95% confidence interval: [1.602-16.519]).
Conclusion: More than one-fourth of the patients who underwent TT insertion for OME developed recurrence. Tympanostomy tube extrusion earlier than 12 months was associated with a higher recurrence rate. Small TTs increased the probability of early TT extrusion.
Keywords: extrusion; otitis media; predictors; recurrence; tympanostomy; ventilation tube.
Copyright: © Saudi Medical Journal.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Otitis media with effusion: recurrence after tympanostomy tube extrusion.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2010 Mar;74(3):271-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2009.11.035. Epub 2009 Dec 30. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2010. PMID: 20044147
-
Analysis of Paparella Type 1 tympanostomy tubes in pediatric patients: A single-center retrospective review.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Dec;175:111751. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2023.111751. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 37839293
-
Comparison of extrusion and patency of silicon versus thermoplastic elastomer tympanostomy tubes.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2019 Jun;46(3):311-318. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2018.09.002. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2019. PMID: 30228034 Clinical Trial.
-
Risk Factors for Multiple Tympanostomy Tube Placements in Children: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Laryngoscope. 2021 Jul;131(7):E2363-E2370. doi: 10.1002/lary.29342. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Laryngoscope. 2021. PMID: 33382113
-
Outcomes of in-office versus operating room insertion of tympanostomy tubes in children.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Dec;175:111772. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2023.111772. Epub 2023 Oct 24. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 37898011 Review.
References
-
- Engel JA, Straetemans M, Zielhuis GA.. Birth characteristics and recurrent otitis media with effusion in young children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2005; 69: 533–540. - PubMed
-
- Tos M. Epidemiology and natural history of secretory otitis. Am J Otol 1984; 5: 459–462. - PubMed
-
- Rosenfeld RM, Shin JJ, Schwartz SR, Coggins R, Gagnon L, Hackell JM, et al. Clinical practice guideline: otitis media with effusion (update). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2016; 154: S1–S41. - PubMed
-
- Paradise JL, Rockette HE, Colborn DK, Bernard BS, Smith CG, Kurs-Lasky M, et al. Otitis media in 2253 Pittsburgh-area infants: prevalence and risk factors during the first 2 years of life. Pediatrics 1997; 99: 318–333. - PubMed
-
- Alaraifi AK, Alosfoor MA, Alsaab F.. Impact of pediatric obesity on the prevalence and outcome of otitis media with effusion. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2020; 133: 110005. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources