Concomitant Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Type 1 Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Potential Issue in the Diagnosis of Carcinoma by Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Fine-needle Biopsy
- PMID: 35831103
- PMCID: PMC10017232
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0075-22
Concomitant Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Type 1 Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Potential Issue in the Diagnosis of Carcinoma by Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Fine-needle Biopsy
Abstract
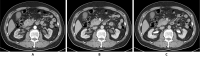
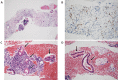
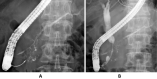
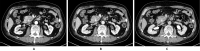
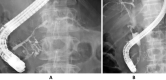
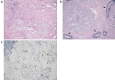
We herein report a 64-year-old man with concomitant pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP). An endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy (EUS-FNB) from the pancreatic head mass revealed level 2 histology of AIP and atypical glands. We diagnosed definitive focal AIP using the clinical diagnostic criteria. Computed tomography revealed that the pancreatic mass had not been reduced by steroid therapy. Surgery was performed after a histological PDAC diagnosis was made via a transpapillary biliary biopsy. The resected specimen revealed PDAC associated with AIP. It is important to consider the cooccurrence of PDAC and AIP even if the histological diagnosis via an EUS-FNB is AIP.
Keywords: autoimmune pancreatitis; endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; steroid pulse therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma with Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Case Report and Literature Review.Intern Med. 2025 May 15;64(10):1525-1533. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.4361-24. Epub 2024 Oct 25. Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 39462595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concordance of the histological diagnosis of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis and its distinction from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle biopsy specimens: an interobserver agreement study.Virchows Arch. 2022 Mar;480(3):565-575. doi: 10.1007/s00428-021-03236-w. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Virchows Arch. 2022. PMID: 34820715
-
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic sampling for the histopathological diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis.Dig Endosc. 2022 Mar;34(3):420-427. doi: 10.1111/den.14076. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Dig Endosc. 2022. PMID: 34233051 Review.
-
Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy using 22-gauge needle in diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis.Dig Liver Dis. 2011 Nov;43(11):869-74. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2011.05.021. Epub 2011 Jul 5. Dig Liver Dis. 2011. PMID: 21733766
-
Efficacy and limitations of the histological diagnosis of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis with endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle biopsy with large tissue amounts.Pancreatology. 2020 Jul;20(5):834-843. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2020.05.026. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Pancreatology. 2020. PMID: 32624418
Cited by
-
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma with Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Case Report and Literature Review.Intern Med. 2025 May 15;64(10):1525-1533. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.4361-24. Epub 2024 Oct 25. Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 39462595 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shimosegawa T, Chari ST, Frulloni L, et al. . International consensus diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis: guidelines of the International Association of Pancreatology. Pancreas 40: 352-358, 2011. - PubMed
-
- Kanno A, Ishida K, Hamada S, et al. . Diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis by EUS-FNA by using a 22-gauge needle based on the international consensus diagnostic criteria. Gastrointest Endosc 76: 594-602, 2012. - PubMed
-
- Kanno A, Masamune A, Fujishima F, et al. . Diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis by EUS-guided FNA using a 22-gauge needle: a prospective multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc 84: 797-804, 2016. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

