Targeting sphingosine kinase 1/2 by a novel dual inhibitor SKI-349 suppresses non-small cell lung cancer cell growth
- PMID: 35831279
- PMCID: PMC9279331
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-022-05049-4
Targeting sphingosine kinase 1/2 by a novel dual inhibitor SKI-349 suppresses non-small cell lung cancer cell growth
Abstract
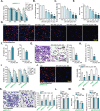
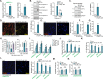
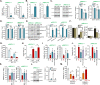
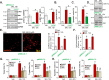
Sphingosine kinase 1 (SphK1) and sphingosine kinase (SphK2) are both important therapeutic targets of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). SKI-349 is a novel, highly efficient and small molecular SphK1/2 dual inhibitor. Here in primary human NSCLC cells and immortalized cell lines, SKI-349 potently inhibited cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, migration and viability. The dual inhibitor induced mitochondrial depolarization and apoptosis activation in NSCLC cells, but it was non-cytotoxic to human lung epithelial cells. SKI-349 inhibited SphK activity and induced ceramide accumulation in primary NSCLC cells, without affecting SphK1/2 expression. SKI-349-induced NSCLC cell death was attenuated by sphingosine-1-phosphate and by the SphK activator K6PC-5, but was potentiated by the short-chain ceramide C6. Moreover, SKI-349 induced Akt-mTOR inactivation, JNK activation, and oxidative injury in primary NSCLC cells. In addition, SKI-349 decreased bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) expression and downregulated BRD4-dependent genes (Myc, cyclin D1 and Klf4) in primary NSCLC cells. At last, SKI-349 (10 mg/kg) administration inhibited NSCLC xenograft growth in nude mice. Akt-mTOR inhibition, JNK activation, oxidative injury and BRD4 downregulation were detected in SKI-349-treated NSCLC xenograft tissues. Taken together, targeting SphK1/2 by SKI-349 potently inhibits NSCLC cell growth in vitro and in vivo.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeting SphK1/2 by SKI-178 inhibits prostate cancer cell growth.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Aug 21;14(8):537. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06023-4. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37604912 Free PMC article.
-
The sphingosine kinase inhibitor SKI-V suppresses cervical cancer cell growth.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Apr 18;18(7):2994-3005. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.71381. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35541904 Free PMC article.
-
GDC-0349 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell growth.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Nov 5;11(11):951. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03146-w. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 33154352 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting sphingosine kinase-1 to inhibit melanoma.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012 Mar;25(2):259-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-148X.2012.00970.x. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012. PMID: 22236408 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA HULC promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and inhibits the apoptosis by up-regulating sphingosine kinase 1 (SPHK1) and its downstream PI3K/Akt pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Dec;22(24):8722-8730. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201812_16637. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30575912
Cited by
-
Targeting SphK1/2 by SKI-178 inhibits prostate cancer cell growth.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Aug 21;14(8):537. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06023-4. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37604912 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA Monitoring in Human Alveolar Macrophages from Patients with Smoking-Related Lung Diseases: A Preliminary Study.Biomedicines. 2024 May 9;12(5):1050. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12051050. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38791013 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting variation in the somatic mutation landscape of non-small cell lung cancer.HGG Adv. 2025 Apr 10;6(2):100420. doi: 10.1016/j.xhgg.2025.100420. Epub 2025 Feb 24. HGG Adv. 2025. PMID: 40007122 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals aberrant sphingolipid metabolism in non-small cell lung cancer impacts tumor-associated macrophages and stimulates angiogenesis via macrophage inhibitory factor signaling.Thorac Cancer. 2024 May;15(14):1164-1175. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15283. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Thorac Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38587042 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting POLRMT by IMT1 inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Sep 3;15(9):643. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07023-8. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39227564 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

