Efficacy of auranofin as an inhibitor of desmoid progression
- PMID: 35831372
- PMCID: PMC9279441
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-15756-9
Efficacy of auranofin as an inhibitor of desmoid progression
Abstract
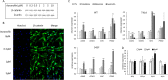
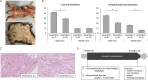
Anticancer drugs and molecular targeted therapies are used for refractory desmoid-type fibromatosis (DF), but occasionally cause severe side effects. The purpose of this study was to identify an effective drug with fewer side effects against DF by drug repositioning, and evaluate its efficacy. FDA-approved drugs that inhibit the proliferation of DF cells harboring S45F mutations of CTNNB1 were screened. An identified drug was subjected to the investigation of apoptotic effects on DF cells with analysis of Caspase 3/7 activity. Expression of β-catenin was evaluated with western blot analysis, and immunofluorescence staining. Effects of the identified drug on in vivo DF were analyzed using Apc1638N mice. Auranofin was identified as a drug that effectively inhibits the proliferation of DF cells. Auranofin did not affect Caspase 3/7 activity compared to control. The expression level of β-catenin protein was not changed regardless of auranofin concentration. Auranofin effectively inhibited the development of tumorous tissues by both oral and intraperitoneal administration, particularly in male mice. Auranofin, an anti-rheumatic drug, was identified to have repositioning effects on DF. Since auranofin has been used for many years as an FDA-approved drug, it could be a promising drug with fewer side effects for DF.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

