Presence of specific SARS-COV2 antibodies in hemodialysis patients and their caregivers after the first wave of COVID-19
- PMID: 35831388
- PMCID: PMC9279503
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-15913-0
Presence of specific SARS-COV2 antibodies in hemodialysis patients and their caregivers after the first wave of COVID-19
Abstract
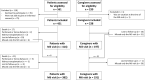
Hemodialysis (HD) patients are at risk for severe COVID-19 and cannot comply with social distancing. SARS-COV2 seroprevalence in French patients and caregivers after the first wave of COVID-19 is unknown. SeroCOVIDial is a prospective study conducted between June and December 2020. SARS-COV2 seroprevalence was evaluated by a rapid serological test (BIOSYNEX) in HD patients and caregivers, and the presence or not of anti-SARS-COV2 neutralizing or non-neutralizing antibodies in patients was also determined by ELISA and seroneutralization. In June 2020, 451 HD patients and 238 caregivers were included. Overall SARS-COV2 seroprevalence was 8.4% (patients) and 6.7% (caregivers), and was 87.1% (patients) and 90.0% (caregivers) in participants with a previously documented SARS-COV2 infection. Overall seroprevalence reached 13.8% (patients) and 12.6% (caregivers) following the second epidemic wave. During the follow-up, 38 (8.4%) patients died (9 of COVID-19). Among the 44 (10.6%) patients who became infected, only two were seropositive at M0. The levels of anti-SARS-COV2 antibodies decreased over time in patients and caregivers. The BIOSYNEX test showed 82.9% sensitivity and 97.7% specificity. Prevalence of anti-SARS-COV2 antibodies was low in HD patients and caregivers after the first epidemic wave but rose after the second wave. A rapid serological test showed good performances and could be useful for future monitoring of anti-SARS-COV2 antibodies.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Jager KJ, Kramer A, Chesnaye NC, Couchoud C, Sánchez-Álvarez JE, Garneata L, et al. Results from the ERA-EDTA Registry indicate a high mortality due to COVID-19 in dialysis patients and kidney transplant recipients across Europe. Kidney Int. 2020;98:1540–1548. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.09.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous