Comparison of NUCLEOCOUNTER, ANDROVISION with Leja chambers and the newly developed ANDROVISION eFlow for sperm concentration analysis in boars
- PMID: 35831488
- PMCID: PMC9279483
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-16280-6
Comparison of NUCLEOCOUNTER, ANDROVISION with Leja chambers and the newly developed ANDROVISION eFlow for sperm concentration analysis in boars
Abstract
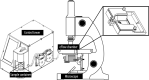
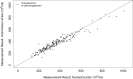
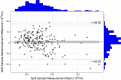
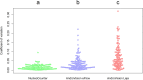
Exact analysis of sperm concentration in raw and diluted semen is of major importance in swine artificial insemination, as sperm concentration is one of the most important characteristics of an ejaculate determining the value of the ejaculate and the productive life of the boar. The study compares different methods for sperm concentration analysis in raw and diluted boar semen: NUCLEOCOUNTER SP-100, the ANDROVISION with Leja chambers and the new ANDROVISION eFlow system. The Concordance Correlation Coefficient (CCC) between NUCLEOCOUNTER and ANDROVISION eFlow was 0.955 for raw (n = 185 ejaculates) and 0.94 for diluted semen (n = 109 ejaculates). The CCC between NUCLEOCOUNTER and ANDROVISION with Leja chambers was 0.66. A Bland-Altman plot of split-sample measurements of sperm concentration with NUCLEOCOUNTER and ANDROVISION eFlow showed that 95.1% of all measurements lay within ± 1.96 standard deviation. The coefficients of variance were 1.6 ± 1.3%, 3.6 ± 3.6% and 7.3 ± 6.3% for NUCLEOCOUNTER, ANDROVISION eFlow and ANDROVISION with Leja chambers in diluted semen, respectively. NUCLEOCOUNTER and ANDROVISION eFlow are comparable tools to measure the concentration of raw and diluted boar semen. In comparison to ANDROVISION with Leja chambers, concentration analyses of diluted semen using NUCLEOCOUNTER or ANDROVISION eFlow show a higher repeatability within and a higher concordance between the methods.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validation of a portable device (iSperm® ) for the assessment of stallion sperm motility and concentration.Reprod Domest Anim. 2019 Aug;54(8):1113-1120. doi: 10.1111/rda.13487. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Reprod Domest Anim. 2019. PMID: 31177582
-
Comparison of different methods for assessment of sperm concentration and membrane integrity with bull semen.J Androl. 2009 Nov-Dec;30(6):661-8. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.108.007500. Epub 2009 May 28. J Androl. 2009. PMID: 19478330
-
Differences in CASA output according to the chamber type when analyzing frozen-thawed bull sperm.Anim Reprod Sci. 2016 Mar;166:72-9. doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2016.01.005. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Anim Reprod Sci. 2016. PMID: 26791331
-
In Vitro Measures for Assessing Boar Semen Fertility.Reprod Domest Anim. 2015 Jul;50 Suppl 2:20-4. doi: 10.1111/rda.12533. Reprod Domest Anim. 2015. PMID: 26174915 Review.
-
New Approaches to Boar Semen Evaluation, Processing and Improvement.Reprod Domest Anim. 2015 Jul;50 Suppl 2:11-9. doi: 10.1111/rda.12554. Reprod Domest Anim. 2015. PMID: 26174914 Review.
Cited by
-
Boar Semen Assessment for the Production of Artificial Insemination Doses.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2897:93-108. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4406-5_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40202630
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

