Reconstitution of a telomeric replicon organized by CST
- PMID: 35831508
- PMCID: PMC9402439
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04930-8
Reconstitution of a telomeric replicon organized by CST
Abstract
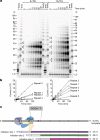
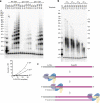
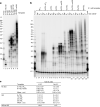
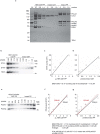
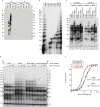
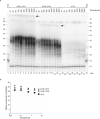
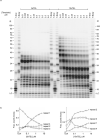
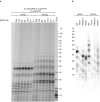
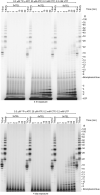
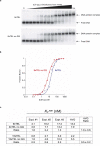
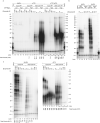
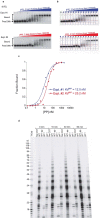
Telomeres, the natural ends of linear chromosomes, comprise repeat-sequence DNA and associated proteins1. Replication of telomeres allows continued proliferation of human stem cells and immortality of cancer cells2. This replication requires telomerase3 extension of the single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) of the telomeric G-strand ((TTAGGG)n); the synthesis of the complementary C-strand ((CCCTAA)n) is much less well characterized. The CST (CTC1-STN1-TEN1) protein complex, a DNA polymerase α-primase accessory factor4,5, is known to be required for telomere replication in vivo6-9, and the molecular analysis presented here reveals key features of its mechanism. We find that human CST uses its ssDNA-binding activity to specify the origins for telomeric C-strand synthesis by bound Polα-primase. CST-organized DNA polymerization can copy a telomeric DNA template that folds into G-quadruplex structures, but the challenges presented by this template probably contribute to telomere replication problems observed in vivo. Combining telomerase, a short telomeric ssDNA primer and CST-Polα-primase gives complete telomeric DNA replication, resulting in the same sort of ssDNA 3' overhang found naturally on human telomeres. We conclude that the CST complex not only terminates telomerase extension10,11 and recruits Polα-primase to telomeric ssDNA4,12,13 but also orchestrates C-strand synthesis. Because replication of the telomere has features distinct from replication of the rest of the genome, targeting telomere-replication components including CST holds promise for cancer therapeutics.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
T.R.C. is a scientific advisor for Storm Therapeutics and Eikon Therapeutics. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

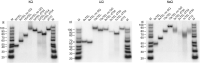
References
-
- Kim NW, et al. Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science. 1994;266:2011–2015. - PubMed
-
- Greider CW, Blackburn EH. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell. 1985;43:405–413. - PubMed
-
- Goulian M, Heard CJ. The mechanism of action of an accessory protein for DNA polymerase α/primase. J. Biol. Chem. 1990;265:13231–13239. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

