Association between lower plasma adiponectin levels and higher liver stiffness in type 2 diabetic individuals with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: an observational cross-sectional study
- PMID: 35831700
- PMCID: PMC9464740
- DOI: 10.1007/s42000-022-00387-6
Association between lower plasma adiponectin levels and higher liver stiffness in type 2 diabetic individuals with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: an observational cross-sectional study
Abstract
Purpose: Little is known about the association between plasma adiponectin levels and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We examined whether there is an association between lower plasma adiponectin levels and the presence/severity of NAFLD in people with T2DM.
Methods: We cross-sectionally recruited 79 men with non-insulin-treated T2DM and no known liver diseases, who had consecutively attended our diabetes outpatient service over a 6-month period and who underwent both ultrasonography and Fibroscan-measured liver stiffness (LSM). Nine single nucleotide polymorphisms (PNPLA3 rs738409 and other genetic variants) associated with NAFLD were investigated.
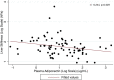
Results: Among the 79 participants included (mean age 67 ± 10 years, BMI 27.7 ± 4 kg/m2), 28 did not have NAFLD, 32 had steatosis alone, and 19 had NAFLD with coexisting significant fibrosis (LSM ≥ 7.0 kPa by Fibroscan®). Compared to those without NAFLD, patients with hepatic steatosis alone and those with hepatic steatosis and coexisting significant fibrosis had lower high-molecular-weight adiponectin levels (5.5 [IQR 2.3-7.6] vs. 2.4 [1.8-3.7] vs. 1.6 [1.0-2.9] µg/mL; p < 0.001). After adjustment for age, body mass index, insulin resistance, and the PNPLA3 rs738409 variant, lower plasma adiponectin levels were found to be associated with increased odds of both steatosis alone (adjusted-odds ratio [OR] 2.44, 95% CI 1.04-5.56, p = 0.042) and NAFLD with coexisting significant fibrosis (adjusted-OR 3.84, 95% CI 1.23-10.0, p = 0.020). Similar findings were observed after adjustment for the other eight genotyped NAFLD-related polymorphisms.
Conclusion: Lower plasma adiponectin levels are closely associated with the presence and severity of NAFLD in men with T2DM, pointing to a role of adiponectin in NAFLD development and progression.
Keywords: Hypoadiponectinemia; Liver fibrosis; NAFLD; NASH; Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver, European Association for the Study of Diabetes, European Association for the Study of Obesity. EASL-EASD-EASO clinical practice guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol 2016;64:1388–402. - PubMed
-
- Le MH, Yeo YH, Li X, et al. 2019 Global NAFLD prevalence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical