Effects of SARS-CoV-2 infections in patients with cancer on mortality, ICU admission and incidence: a systematic review with meta-analysis involving 709,908 participants and 31,732 cancer patients
- PMID: 35831763
- PMCID: PMC9281353
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-022-04191-y
Effects of SARS-CoV-2 infections in patients with cancer on mortality, ICU admission and incidence: a systematic review with meta-analysis involving 709,908 participants and 31,732 cancer patients
Abstract
Background: Cancer patients constitute one of the highest-risk patient groups during the COVID-19 pandemic. In this study, it was aimed to perform a systematic review and meta-analysis to determine both the incidence and ICU (Intensive Care Unit) admission rates and mortality in SARS-CoV-2 infected cancer patients.
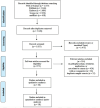
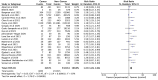
Methods: The PRISMA guidelines were closely followed during the design, analysis, and reporting of this systematic review and meta-analysis. A comprehensive literature search was performed for the published papers in PubMed/Medline, Scopus, medRxiv, Embase, and Web of Science (WoS) databases. SARS-CoV-2 infection pooled incidence in the cancer populations and the risk ratio (RR) of ICU admission rates/mortality in cancer and non-cancer groups, with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), were calculated using the random-effects model.
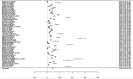
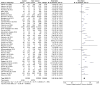
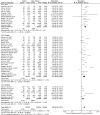
Results: A total of 58 studies, involving 709,908 participants and 31,732 cancer patients, were included in this study. The incidence in cancer patients was calculated as 8% (95% CI: 8-9%). Analysis results showed that mortality and ICU admission rate was significantly higher in patients with cancer (RR = 2.26, 95% CI: 1.94-2.62, P < 0.001; RR = 1.45, 95% CI: 1.28-1.64, p < 0.001, respectively).
Conclusion: As a result, cancer was an important comorbidity and risk factor for all SARS-CoV-2 infected patients. This infection could result in severe and even fatal events in cancer patients. Cancer is associated with a poor prognosis in the COVID-19 pandemic. Cancer patients should be assessed more sensitively in the COVID-19 outbreak.
Keywords: Cancer; ICU admission; Mortality; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adejumo OA, Ogunniyan T, Adesola S, Gordon I, Oluwadun OB, Oladokun OD et al (2021) Clinical presentation of COVID-19-positive and-negative patients in Lagos Nigeria: a comparative study. Niger Postgrad Med J 28:75. 10.4103/npmj.npmj_547_21 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

