Risk factors and mortality for elderly patients with bloodstream infection of carbapenem resistance Klebsiella pneumoniae: a 10-year longitudinal study
- PMID: 35831805
- PMCID: PMC9281020
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-022-03275-1
Risk factors and mortality for elderly patients with bloodstream infection of carbapenem resistance Klebsiella pneumoniae: a 10-year longitudinal study
Abstract
Background: Bloodstream infection (BSI) caused by carbapenem resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP), especially in elderly patients, results in higher morbidity and mortality. The purpose of this study was to assess risk factors associated with CRKP BSI and short-term mortality among elderly patients in China.
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, we enrolled 252 inpatients aged ≥ 65 years with BSI caused by KP from January 2011 to December 2020 in China. Data regarding demographic, microbiological characteristics, and clinical outcome were collected.
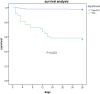
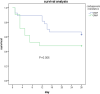
Result: Among the 252 BSI patients, there were 29 patients (11.5%) caused by CRKP and 223 patients (88.5%) by carbapenem-susceptible KP (CSKP). The overall 28-day mortality rate of elderly patients with a KP BSI episode was 10.7% (27/252), of which CRKP BSI patients (14 / 29, 48.3%) were significantly higher than CSKP patients (13 / 223, 5.83%) (P < 0.001). Hypertension (OR: 13.789, [95% CI: 3.883-48.969], P < 0.001), exposure to carbapenems (OR: 8.073, [95% CI: 2.066-31.537], P = 0.003), and ICU stay (OR: 11.180, [95% CI: 2.663-46.933], P = 0.001) were found to be associated with the development of CRKP BSI in elderly patients. A multivariate analysis showed that isolation of CRKP (OR 2.881, 95% CI 1.228-6.756, P = 0.015) and KP isolated in ICU (OR 11.731, 95% CI 4.226-32.563, P < 0.001) were independent risk factors for 28-day mortality of KP BSI.
Conclusion: In elderly patients, hypertension, exposure to carbapenems and ICU stay were associated with the development of CRKP BSI. Active screening of CRKP for the high-risk populations, especially elderly patients, is significant for early detection and successful management of CRKP infection.
Keywords: Bloodstream infection; Carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae; Elderly patients; Mortality; Risk factor.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Stewardson AJ, Marimuthu K, Sengupta S, Allignol A, El-Bouseary M, Carvalho MJ, Hassan B, Delgado-Ramirez MA, Arora A, Bagga R, et al. Effect of carbapenem resistance on outcomes of bloodstream infection caused by Enterobacteriaceae in low-income and middle-income countries (PANORAMA): a multinational prospective cohort study. LANCET INFECT DIS. 2019;19(6):601–610. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30792-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tacconelli E, Carrara E, Savoldi A, Harbarth S, Mendelson M, Monnet DL, Pulcini C, Kahlmeter G, Kluytmans J, Carmeli Y, et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: the WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. LANCET INFECT DIS. 2018;18(3):318–327. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30753-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schwaber MJ, Klarfeld-Lidji S, Navon-Venezia S, Schwartz D, Leavitt A, Carmeli Y. Predictors of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae acquisition among hospitalized adults and effect of acquisition on mortality. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008;52(3):1028–1033. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01020-07. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical