3D culturing of human pluripotent stem cells-derived endothelial cells for vascular regeneration
- PMID: 35832092
- PMCID: PMC9254250
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.69938
3D culturing of human pluripotent stem cells-derived endothelial cells for vascular regeneration
Abstract
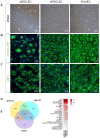
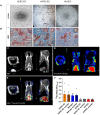
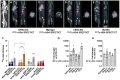
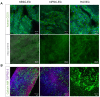
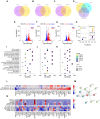
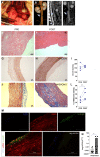
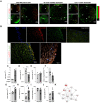
Rationale: Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived endothelial cells can be candidates for engineering therapeutic vascular grafts. Methods: Here, we studied the role of three-dimensional culture on their characteristics and function both in vitro and in vivo. Results: We found that differentiated hPSC-EC can re-populate decellularized biomatrices; they remain viable, undergo maturation and arterial/venous specification. Human PSC-EC develop antifibrotic, vasoactive and anti-inflammatory properties during recellularization. In vivo, a robust increase in perfusion was detected at the engraftment sites after subcutaneous implantation of an hPSC-EC-laden hydrogel in rats. Histology confirmed survival and formation of capillary-like structures, suggesting the incorporation of hPSC-EC into host microvasculature. In a canine model, hiPSC-EC-seeded onto decellularised vascular segments were functional as aortic grafts. Similarly, we showed the retention and maturation of hiPSC-EC and dynamic remodelling of the vessel wall with good maintenance of vascular patency. Conclusions: A combination of hPSC-EC and biomatrices may be a promising approach to repair ischemic tissues.
Keywords: angiogenesis tracking; endothelial cells; human pluripotent stem cells; multimodality imaging; tissue-engineered vascular grafts.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: DM is managing director, CROmed Research Ltd, grant-in-aid of Mediso Ltd. by providing nanoScan PET-MRI instrument usage time.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2014, in 2015. - PubMed
-
- Slovut DP, Lipsitz EC. Surgical technique and peripheral artery disease. Circulation. 2012;126:1127–38. - PubMed
-
- Isenberg BC, Williams C, Tranquillo RT. Small-diameter artificial arteries engineered in vitro. Circ Res. 2006;98:25–35. - PubMed
-
- Seifu DG, Purnama A, Mequanint K, Mantovani D. Small-diameter vascular tissue engineering. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2013;10:410–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

