Elevated highly sensitive C-reactive protein in fibromyalgia associates with symptom severity
- PMID: 35832286
- PMCID: PMC9272915
- DOI: 10.1093/rap/rkac053
Elevated highly sensitive C-reactive protein in fibromyalgia associates with symptom severity
Abstract
Objectives: Fibromyalgia (FM), a common pain syndrome, is thought to be a non-inflammatory, nociplastic condition, but evidence implicating neuroinflammation has been increasing. Systemic inflammation may be associated with more severe symptoms in some FM patients. We studied healthy controls and FM patients with and without systemic inflammation detectable using high-sensitivity CRP (hsCRP) measurement.
Methods: We measured hsCRP levels and gathered clinical and questionnaire data [including the Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire (FIQ)] from 40 female FM patients and 30 age-matched healthy women. An hsCRP level >3 mg/l was considered elevated.
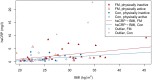
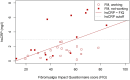
Results: FM patients had significantly higher mean hsCRP levels than controls, explained by overweight and lower leisure-time physical activity. Eight FM patients had elevated hsCRP levels and 29 had normal hsCRP levels. Levels of hsCRP were significantly correlated with FIQ scores. Patients with elevated hsCRP had higher FIQ scores, with worse physical functioning and greater pain and were less likely to be employed than patients with normal hsCRP. These patient groups did not differ by blood count, liver function or lipid profiles, nor by education, psychological measures, sleep disturbance, smoking or comorbidities.
Conclusion: Some FM patients have elevated hsCRP, mostly due to overweight and physical inactivity. They have worse symptoms and their ability to work is impaired. Measurement of hsCRP may help to identify FM patients in greatest need of interventions supporting working ability.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov (https://clinicaltrials.gov), NCT03300635.
Keywords: CRP; FM; chronic pain; hsCRP; inflammation; widespread pain.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures
References
-
- Inanici F, Yunus MB.. History of fibromyalgia: past to present. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2004;8:369–78. - PubMed
-
- Kosek E, Cohen M, Baron R. et al. Do we need a third mechanistic descriptor for chronic pain states? Pain 2016;157:1382–6. - PubMed
-
- Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB. et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of fibromyalgia. Report of the multicenter criteria committee. Arthritis Rheum 1990;33:160–72. - PubMed
-
- Wolfe F, Clauw DJ, Fitzcharles MA. et al. 2016 Revisions to the 2010/2011 fibromyalgia diagnostic criteria. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2016;46:319–29. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
