Leprosy: A Review of Epidemiology, Clinical Diagnosis, and Management
- PMID: 35832335
- PMCID: PMC9273393
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8652062
Leprosy: A Review of Epidemiology, Clinical Diagnosis, and Management
Abstract
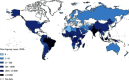
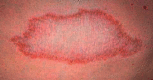
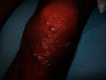
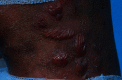
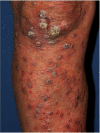
Leprosy is a neglected infectious disease caused by acid-fast bacillus Mycobacterium leprae. It primarily affects the skin and then progresses to a secondary stage, causing peripheral neuropathy with potential long-term disability along with stigma. Leprosy patients account for a significant proportion of the global disease burden. Previous efforts to improve diagnostic and therapeutic techniques have focused on leprosy in adults, whereas childhood leprosy has been relatively neglected. This review aims to update the diagnostic and therapeutic recommendations for adult and childhood leprosy. This review summarizes the clinical, bacteriological, and immunological approaches used in the diagnosis of leprosy. As strategies for the diagnosis and management of leprosy continue to develop better and more advanced knowledge, control and prevention of leprosy are crucial.
Copyright © 2022 Kou-Huang Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Paige C. F., Truman R. W., Scholl D. T. Prevalence and incidence density of Mycobacterium leprae and Trypanosoma cruzi infections within a population of wild nine-banded armadillos. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene . 2002;67(5):528–532. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2002.67.528. - DOI - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Leprosy. 2022. https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leprosy .
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Global leprosy situation, 2010. Weekly Epidemiological Record . 2010;85(35):337–348.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

