Evaluation of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging in Differentiating Benign and Malignant Cervical Lymphadenopathy
- PMID: 35832364
- PMCID: PMC9272720
- DOI: 10.4103/JMU.JMU_10_21
Evaluation of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging in Differentiating Benign and Malignant Cervical Lymphadenopathy
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to assess the diagnostic role of acoustic radiation force impulse imaging (ARFI) in differentiating benign and malignant cervical nodes.
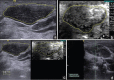
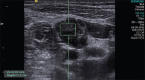
Methods: This was a diagnostic accuracy cross-sectional study. All patients who underwent ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) of cervical nodes were included. Patients without FNAC/biopsy and patients in whom cervical nodes were cystic or completely necrotic were excluded. FNAC was used as reference investigation to predict the diagnostic accuracy. In all cases, FNAC was carried out after the B-mode, color Doppler and the ARFI imaging. In patients with multiple cervical lymph nodes, the most suspicious node based on grayscale findings was chosen for ARFI. ARFI included Virtual Touch imaging (VTI), area ratio (AR), and shear wave velocity (SWV) for each node, and the results were compared with FNAC/biopsy.
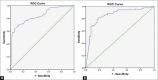
Results: The final analysis included 166 patients. Dark VTI elastograms had sensitivity and specificity of 86.2% and 72.1%, respectively, in identifying malignant nodes. Sensitivity and specificity of AR were 71.3% and 82.3%, respectively, for a cutoff of 1.155. Median SWV of benign and malignant nodes was 1.9 [95% confidence interval (CI), 1.56-2.55] m/s and 6.7 (95% CI, 2.87-9.10) m/s, respectively. SWV >2.68 m/s helped in identifying malignant nodes with 81% specificity, 81.6% sensitivity, and 81.3% accuracy. ARFI was found to be inaccurate in tuberculous and lymphomatous nodes.
Conclusion: Malignant nodes had significantly darker elastograms, higher AR and SWV compared to benign nodes, and SWV was the most accurate parameter. ARFI accurately identifies malignant nodes, hence could potentially avoid unwarranted biopsy.
Keywords: Acoustic radiation force impulse; Virtual Touch imaging; acoustic radiation force impulse imaging; area ratio; cervical lymph nodes; shear wave velocity.
Copyright: © 2021 Journal of Medical Ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ahuja AT, Ying M. Sonographic evaluation of cervical lymph nodes. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005;184:1691–9. - PubMed
-
- Teng DK, Wang H, Lin YQ, Sui GQ, Guo F, Sun LN. Value of ultrasound elastography in assessment of enlarged cervical lymph nodes. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13:2081–5. - PubMed
-
- Lyshchik A, Higashi T, Asato R, Tanaka S, Ito J, Hiraoka M, et al. Cervical lymph node metastases: Diagnosis at sonoelastography – Initial experience 1. Radiology. 2007;243:258–67. - PubMed
-
- Shozushima M, Suzuki M, Nakasima T, Yanagisawa Y, Sakamaki K, Takeda Y. Ultrasound diagnosis of lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 1990;19:165–70. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
