Availability Bias and the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Case Study of Legionella Pneumonia
- PMID: 35832749
- PMCID: PMC9273171
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.25846
Availability Bias and the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Case Study of Legionella Pneumonia
Abstract
Cognitive biases, such as the availability heuristic or availability bias, can inadvertently affect patient outcomes. These biases may be magnified during times of heightened awareness of a particular disease. Failure to identify cognitive biases when managing patients during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic can delay the institution of the right treatment option and result in poor health outcomes. We present a case of delayed diagnosis of Legionella pneumonia due to COVID-19-related availability bias. We discuss some methods to mitigate the effects of this bias and the importance of challenging trainees to recognize these pitfalls in medical training.
Keywords: availability bias; availability heuristic; cognitive biases; coronavirus disease 2019 (covid-19); covid-19 pandemic; legionella pneumonia; legionellosis; sars-cov-2.
Copyright © 2022, Kyere et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
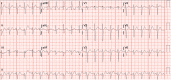
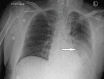
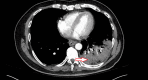
References
-
- Classification of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium: Legionella pneumophila, genus novum, species nova, of the family Legionellaceae, familia nova. Brenner DJ, Steigerwalt AG, McDade JE. Ann Intern Med. 1979;90:656–658. - PubMed
-
- Legionnaires' disease: description of an epidemic of pneumonia. Fraser DW, Tsai TR, Orenstein W, et al. N Engl J Med. 1977;297:1189–1197. - PubMed
-
- Legionnaires' disease: isolation of a bacterium and demonstration of its role in other respiratory disease. McDade JE, Shepard CC, Fraser DW, Tsai TR, Redus MA, Dowdle WR. N Engl J Med. 1977;297:1197–1203. - PubMed
-
- Incidence of community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization: results of a population-based active surveillance study in Ohio. Marston BJ, Plouffe JF, File TM, et al. Arch Intern Med. 1997;157:1709–1718. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
